cx28394 Conexant Systems, Inc., cx28394 Datasheet - Page 93

cx28394
Manufacturer Part Number
cx28394
Description
Quad/x16/octal-t1/e1/j1 Framers
Manufacturer
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet
1.CX28394.pdf
(305 pages)
- Current page: 93 of 305
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
CX28394/28395/28398
Quad/x16/Octal—T1/E1/J1 Framers
100054E
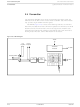
2.3.5. 2 Slip Buffer
2.3.5.1 Timebase
Two-Frame Normal
The TSB timebase synchronizes TPCMI, TFSYNC, TMSYNC, and TINDO with
the Transmit System Bus Clock (TSBCK). The TSBCK can be slaved to three
different clock sources: Transmit Clock Input (TCKI), Transmit System Bus
Clock Input (TSBCKI), and Receive System Bus Clock Input (RSBCKI). The
TSB clock selection is made through the Clock Input Mux register [CMUX; addr
01A]. TCKI is automatically selected when the transmit slip buffer is bypassed.
The system bus clock can also be configured to run at twice the data rate by
setting the X2CLK bit in the System Bus Interface Configuration register
[SBI_CR; addr 0D0] when TSLIP is not in Bypass mode.
configured for either TFSYNC or TMSYNC using the TMSYNC_EN register bit
[PIO; addr 018]. TFSYNC and TMSYNC can be individually configured as
inputs or outputs, [PIO; addr 018]. TFSYNC and TMSYNC should be configured
as inputs when the TSB timebase is slaved to the system bus, the transmit framer
is disabled [TABORT; addr 071], or TSB carries embedded T1 framing.
TFSYNC and TMSYNC should be configured as outputs when the TSB timebase
is master of the system bus, or the transmit framer is enabled. TFSYNC and
TMSYNC can be also configured as rising or falling edge outputs [TSB_CR;
addr 0D4]. In addition to having TFSYNC and TMSYNC active on the frame
boundary, a programmable offset is available to select the time slot and bit offset
in the frame (see Transmit System Bus Sync Time Slot Offset [TSYNC_TS; addr
0D6] and Transmit System Bus Sync Bit Offset [TSYNC_BIT; addr 0D5]).
The 64-byte Transmit PCM Slip Buffer [TSLIP; addr 140 to 17F] resynchronizes
the Transmit System Bus Clock (TSBCK) and data (TPCMI) to the Transmit
Clock (TXCLK) and data (TNRZ). TSLIP acts like an elastic store by clocking
PCM data in on TPCMI with TSBCK and clocking TNRZ data out with TXCLK.
TPCMI can be configured to sample on the rising or falling edge of TSBCKI (see
the Transmit System Bus Configuration register [TSB_CR; addr 0D4]).
Frame Short, and Bypass. TSLIP mode is set in the Transmit System Bus
Configuration register [TSB_CR; addr 0D4]. It is organized as a two-frame
buffer, with high frame and low frame buffers. This allows MPU access to frame
data, regardless of the TSLIP mode selected. Each byte offset into the frame
buffer is a different time slot, offset 0 in TSLIP is always time slot 0 (TS0); offset
1 is always TS1, and so on. The slip buffer has processor read/write access.
In Normal mode, the slip buffer total depth is two 193-bit frames (T1), or two
256-bit frames (E1). Data is written to the slip buffer using TSBCK and read from
the slip buffer using TXCLK. If there is a slight rate difference between the two
clocks, the slip buffer changes from its initial condition—approximately half
full—by either adding or removing frames. If TSBCK writes to the slip buffer
faster than TXCLK reads the data, the buffer becomes full. When the slip buffer
in Normal mode is full, an entire frame of data is deleted. Conversely, if TXCLK
is reading the slip buffer at a faster rate than TSBCK is writing the data, the buffer
will eventually empty, and an entire frame of data is duplicated. When an entire
frame is deleted or duplicated, it is known as a Frame Slip (FSLIP). An FSLIP is
always one full frame of data. The FSLIP status is reported in the Slip Buffer
Status register [SSTAT; addr 0D9].
In Non-Multiplexed mode, the TFSYNC/TMSYNC dual function pin is
TSLIP has four modes of operation: Two Frame Normal, 64-bit Elastic, Two
Conexant
2.0 Circuit Description
2.3 System Bus
2-35
Related parts for cx28394
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Bluetooth RF Transceiver
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Bluetooth RF Transceiver
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
ATM transmitter/receiver with UTOPIA interface
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Service SAR controller
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CN8223EPFATM Transmitter/Receiver with UTOPIA Interface
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Embedded modem family
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Fully integrated T1/E1 framer and line interface
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Flicker-free video encoder
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Home Networking Physical Layer Device with Integrated Analog Front End Circuitry Data Sheet (Preliminary) CX82100-41Home Network Processor (HNP)
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Flicker-free video encoder
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SmartV.XX Modem
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multichannel synchronous communications controller
Manufacturer:
Conexant Systems, Inc.
Datasheet: