ST52F513G3M6 STMicroelectronics, ST52F513G3M6 Datasheet - Page 48

ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST52F513G3M6
Description
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST52F513G3M6.pdf
(136 pages)
Specifications of ST52F513G3M6
Cpu Family
ST52
Device Core Size
8b
Frequency (max)
20MHz
Interface Type
I2C/SCI/SPI
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
8KB
Total Internal Ram Size
256Byte
# I/os (max)
22
Number Of Timers - General Purpose
2
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3.3/5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
On-chip Adc
8-chx10-bit
Instruction Set Architecture
CISC
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
28
Package Type
SO
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6TR
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
ST52510xx ST52513xx
6.3 Programmable Low Voltage Detector
The on-chip Programmable Low Voltage Detector
(PLVD) circuit prevents the processor from falling
into an unpredictable status if the power supply
drops below a certain level.
When Vdd drops below the detection level, the
PLVD causes an internal processor Reset that
remains active as long as Vdd remains below the
trigger level.
The PLVD resets the entire device except the
Power-on Detector and the PLVD itself.
The PLVD can be enabled/disabled at reset by
setting the Option Byte 3 (PLVD_CR) bits.
When Vdd increases above the Trigger Level, the
PLVD reset is deactivated and the user program is
started from the beginning.
The detection levels are programmable by means
of the Option Byte 3 (PLVD_CR). There are three
levels for the PLVD falling voltages (2.9V, 3.4V,
3.9V) and for rising voltages (3.1V, 3.65V, 4.2V).
The hysteresis for each level are respectively 200
mV, 250 mV and 300 mV.
The PLVD circuit will only detect a drop if Vdd
voltage stays below the safe threshold for at least
5 s before activation/deactivation of the PLVD in
order to filter voltage spikes.
Remark: the PLVD function isn’t active when it is
in HALT mode. In that case the device is reset if the
Vdd voltage stays below the threshold of Power
On Reset.
6.4 Power Saving modes
There are two types of Power Saving modes:
WAIT and HALT mode. These conditions may be
entered by using the WAIT or HALT instructions.
6.4.1 Wait Mode. Wait mode places the ICU in a
low power consumption status by stopping the
CPU. All peripherals and the watchdog remain
active. During WAIT mode the Interrupts are
enabled. The ICU remains in Wait mode until an
Interrupt or a RESET occurs, whereupon the
Program Counter jumps to the interrupt service
routine or, if a Reset occurs, to the beginning of the
user program.
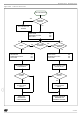
6.4.2 Halt Mode. Halt mode is the lowest ICU
power consumption mode, which is entered by
executing the HALT instruction. The internal
oscillator is turned off, causing all internal
processing to be terminated, including the
operations of the on-chip peripherals. Halt mode
cannot be used when the watchdog is enabled. If
the HALT instruction is executed while the
48/136
watchdog system is enabled, it will be skipped
without modifying the normal CPU operations.
The ICU can exit Halt mode upon reception of an
NMI, a Port Interrupt or a Reset. The internal
oscillator (10 MHZ) is started and a delay period of
4.096 clock cycles is initiated, in order to allow the
oscillator to stabilize and to ensure that recovery
has taken place from the Reset state.
If the device has been configured to work with the
internal clock, the user program is started,
otherwise the Option Byte 7 (WAKEUP) is read
and another count is started before running the
user program. The count duration depends on the
contents of the Option Byte 7 (WAKEUP), that
works as prescaler, according to the following
formula:
This delay has been introduced in order to ensure
that the oscillator has become stable after it is
restarted.
After the start up delay, by exiting with the NMI or
a Port interrupt, the CPU restarts operations by
serving the associated interrupt routine.
Note: if the Port Interrupt is masked, the ICU
doesn’t exit the Halt mode with this interrupt.
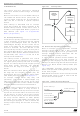
Figure 6.3 WAIT Flow Chart
Delay
CPU CLOCK
PROGRAM COUNTER RESET
=
4096
YES
OSCILLATOR
PERIPHERALS CLOCK
CPU CLOCK
INTERRUPTS
NORMAL PROGRAM FLOW
ON
WAIT ISTRUCTION
WAKEUP
RESET
CPU CLOCK
JUMP TO INT. ROUTINE
INTERRUPT
ON
ON
OFF
ENAB.
NO
+
1
ON
NO
Tclk