ST52F513G3M6 STMicroelectronics, ST52F513G3M6 Datasheet - Page 90

ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST52F513G3M6
Description
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST52F513G3M6.pdf
(136 pages)
Specifications of ST52F513G3M6
Cpu Family
ST52
Device Core Size
8b
Frequency (max)
20MHz
Interface Type
I2C/SCI/SPI
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
8KB
Total Internal Ram Size
256Byte
# I/os (max)
22
Number Of Timers - General Purpose
2
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3.3/5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
On-chip Adc
8-chx10-bit
Instruction Set Architecture
CISC
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
28
Package Type
SO
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6TR
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
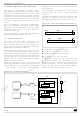
ST52510xx ST52513xx
Note: In 10-bit addressing mode, the comparison
includes the header byte (11110xx0) where xx are
the two most significant bits of the address.
Header matched (10-bit mode only): the interface
generates an acknowledgement pulse if the ACK
bit is set.
Address not matched: the interface ignores it and
waits for another Start condition.
Address matched: the interface generates in
sequence:
– Acknowledge pulse if the ACK bit is set.
– EVF and ADSL bits are set with an interrupt if the
Afterwards, the interface waits for the I2C_SR1
register to be read, holding the SCL line low (see
Figure 14.3
Next, in 7-bit mode read the I2C_IN register to
determine from the least significant bit (Data
Direction Bit) if the slave must enter Receiver or
Transmitter mode.
In 10-bit mode, after receiving the address
sequence the slave is always in receive mode. It
will enter transmit mode on receiving a repeated
Start condition followed by the header sequence
with matching address bits and the least significant
bit set (11110xx1).
Slave Receiver
Following reception of the address and after the
I2C_SR1 register has been read, the slave
receives bytes from the SDA line into the I2C_IN
register via the internal shift register. After each
byte, the interface generates the following in
sequence:
– Acknowledge pulse if the ACK bit is set
– EVF and BTF bits are set with an interrupt if the
Afterwards, the interface waits for the I2C_SR1
register to be read followed by a read of the I2C_IN
register, holding the SCL line low (see
14.3
Slave Transmitter
Following the address reception and after the
I2C_SR1 register has been read, the slave sends
bytes from the I2C_OUT register to the SDA line
via the internal shift register.
The slave waits for a read of the I2C_SR1 register
followed by a write in the I2C_OUT register,
holding the SCL line low (see
Transfer sequencing EV3).
When the acknowledge pulse is received:
– The EVF and BTF bits are set by hardware with
90/136
ITE bit is set.
ITE bit is set.
an interrupt if the ITE bit is set.
Transfer sequencing EV2).
Transfer sequencing EV1).
Figure 14.3
Figure
Closing slave communication
After the last data byte is transferred a Stop
Condition is generated by the master. The
interface detects this condition and sets:
– EVF and STOPF bits with an interrupt if the ITE
Afterwards, the interface waits for a read of the
I2C_SR2 register (see
sequencing EV4).
Error Cases
– BERR: Detection of a Stop or a Start condition
If it is a Stop then the interface discards the data,
releases the lines and waits for another Start
condition.
If it is a Start then the interface discards the data
and waits for the next slave address on the bus.
– AF: Detection of a non-acknowledge bit. In this
Note: In both cases, the SCL line is not held low;
however, SDA line can remain low due to possible
«0» bits transmitted last. At this point, both lines
must be released by software.
How to release the SDA / SCL lines
Set and subsequently clear the STOP bit while
BTF is set. The SDA/SCL lines are released after
the current byte is transferred.
14.4.2 Master Mode.
To switch from default Slave mode to Master mode
a Start condition generation is needed.
Start condition
Setting the START bit while the BUSY bit is
cleared causes the interface to switch to Master
mode (M/SL bit set) and generates a Start
condition.
Once the Start condition is sent:
– The EVF and SB bits are set by hardware with
Afterwards, the master waits for a read of the
I2C_SR1 register followed by a write in the
I2C_OUT register with the Slave address, holding
the SCL line low (see
sequencing EV5).
bit is set.
during a byte transfer. In this case, the EVF and
the BERR bits are set with an interrupt if the ITE
bit is set.
case, the EVF and AF bits are set with an inter-
rupt if the ITE bit is set.
an interrupt if the ITE bit is set.
Figure 14.3
Figure 14.3
Transfer
Transfer