ST52F513G3M6 STMicroelectronics, ST52F513G3M6 Datasheet - Page 98

ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer Part Number
ST52F513G3M6
Description
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST52F513G3M6.pdf
(136 pages)
Specifications of ST52F513G3M6
Cpu Family
ST52
Device Core Size
8b
Frequency (max)
20MHz
Interface Type
I2C/SCI/SPI
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
8KB
Total Internal Ram Size
256Byte
# I/os (max)
22
Number Of Timers - General Purpose
2
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3.3/5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
On-chip Adc
8-chx10-bit
Instruction Set Architecture
CISC
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
28
Package Type
SO
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ST52F513G3M6TR
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
ST52510xx ST52513xx
15 SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI)
15.1 Introduction
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) allows full-
duplex, synchronous, serial communication with
external devices. An SPI system may consist of a
master, one or more slaves, or a system, in which
devices may be either masters or slaves.
SPI is normally used for communication between
the ICU and external peripherals or another ICU.
Refer to the Pin Description section in this
datasheet for the device-specific pin-out.
15.2 Main Features
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
15.3 General description
SPI is connected to external devices through 4
alternate pins:
– MISO: Master In / Slave Out pin
– MOSI: Master Out / Slave In pin
– SCK: Serial Clock pin
– SS: Slave select pin (if not done through soft-
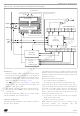
Figure 15.1 SPI Master Slave
98/136
Full duplex, three-wire synchronous transfers
Master or slave operation
Four master mode frequencies
Maximum slave mode frequency = fCKM/4.
Four programmable master bit rates
Programmable clock polarity and phase
End of transfer interrupt flag
Write collision flag protection
Master mode fault protection capability.
ware)
MSBit
8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER
GENERATOR
CLOCK
SPI
MASTER
LSBit
SCK
MOSI
SS
MISO
+5V
A basic example of interconnections between a
single master and a single slave is illustrated in
Figure 15.1
The MOSI pins are connected together as the
MISO pins. In this manner, data is transferred
serially between master and slave (most significant
bit first).
When the master device transmits data to a slave
device via the MOSI pin, the slave device responds
by sending data to the master device via the MISO
pin. This implies full duplex transmission with both
data out and data in synchronized with the same
clock signal (which is provided by the master
device via the SCK pin).
The transmitted byte is replaced by the byte
received and eliminates the need for separate
transmit-empty and receiver-full bits. A status flag
is used to indicate that the I/O operation is
complete.
Four possible data/clock timing relationships may
be chosen (see
must be programmed with the same timing mode.
15.4 Functional Description
Figure 15.2
(SPI) block diagram.
This interface contains 4 dedicated registers:
– A Control Register (SPI_CR)
– A Status Register (SPI_STATUS_CR)
– A Data Register for transmission (SPI_OUT)
– A Data Register for reception (SPI_IN)
15.4.1 Master Configuration.
In a master configuration, the serial clock is
generated on the SCK pin.
MISO
MOSI
SCK
SS
shows the serial peripheral interface
Figure
8-BIT SHIFT REGISTER
MSBit
15.4), but master and slave
SLAVE
LSBit