XC68HC705F32 Motorola, XC68HC705F32 Datasheet - Page 102

XC68HC705F32
Manufacturer Part Number
XC68HC705F32
Description
MICROCONTROLLER
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.XC68HC705F32.pdf
(198 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
- Current page: 102 of 198
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
10
10.2.4
The slave select (SS) input line is used to select a slave device. It must be in the active low state
prior to data transactions and must stay low for the duration of the transaction. The SS line on the
master must be tied high. If it goes low, a mode fault error flag (MODF) is set in the serial peripheral
status register (SPSR). When CPHA = 0, the shift clock is the logical OR of SS and SCK. In this
clock phase mode, SS must go high between successive characters in an SPI message. When
CPHA = 1, SS may be left low for several SPI characters. If there is only one SPI slave MCU, its
SS line may be tied to V
10.3
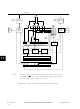
Figure 10-2
device transmits data to a slave device via the MOSI line, the slave device responds by sending
data to the master device via the master’s MISO line. This implies full duplex transmission with
both data out and data in synchronized to the same clock signal. Thus, the byte transmitted is
replaced by the byte received, eliminating the need for separate transmitter-empty and
receiver-full status bits. A single status bit (SPIF) is used to signify that the I/O operation has been
completed.
The SPI is double buffered on read, but not on write. If a write is performed during data transfer,
the transfer is not interrupted, and the write will be unsuccessful. This condition will cause the write
collision status bit (WCOL) in the SPSR to be set. After a data byte is shifted, the SPIF flag in the
SPSR is set.
In master mode, the SCK pin is an output. It idles high or low, depending on the CPOL bit in the
SPCR, until data is written to the shift register. Eight clocks are then generated to shift the eight
bits of data, after which SCK goes idle again.
In slave mode, the slave start logic receives a logic low on the SS pin and a clock input at the SCK
pin, thus synchronizing the slave to the master. Data from the master is received serially via the
slave MOSI line and is loaded into the 8-bit shift register. The data is then transferred, in parallel,
from the 8-bit shift register to the read buffer. During a write cycle, data is written into the shift
register, then the slave waits for a clock train from the master to shift the data out on the slave’s
MISO line.
MOTOROLA
10-4
shows a block diagram of the serial peripheral interface circuitry. When a master
Slave select (SS)
Functional description
SS,
provided CPHA = 1 clock modes are used.
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE
MC68HC05F32
TPG
Related parts for XC68HC705F32
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola, Inc [VOLTAGE REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
3N2046367254 MOTOROLA SC (XSTRS/R F)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MOTOROLA POWERPC 603e MICROPROCESSOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola Semiconductor Datasheet Library
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifier(POWERTAP III Package)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifirer
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> MTE53N50E
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SCHOTTKY BARRIER RECTIFIER 200 AMPERES 60 VOLT
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN SILICON POWER DARLINGTON TRANSISTOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet: