XC68HC705F32 Motorola, XC68HC705F32 Datasheet - Page 140

XC68HC705F32
Manufacturer Part Number
XC68HC705F32
Description
MICROCONTROLLER
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.XC68HC705F32.pdf
(198 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
- Current page: 140 of 198
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
14
14.2.3.7
There is a timer interrupt flag that causes a CPI interrupt from the 32 kHz clock system whenever
set and enabled. The interrupt flag and enable bits are located in the CPI control and status
register (CPICSR). An interrupt will vector to the same interrupt service routine as the core timer
interrupts, located at the address specified by the contents of memory location $FFF8 and $FFF9.
14.2.4
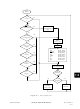
The following three functions (RESET, STOP, and WAIT) are not in the strictest sense interrupts.
However, they are acted upon in a similar manner. Flowcharts for STOP and WAIT are shown in
Figure
RESET: A reset condition causes the program to vector to its starting address, which is contained
in memory locations $FFFE (MSB) and $FFFF (LSB). The I-bit in the condition code register is
also set, to disable interrupts.
STOP: The STOP instruction causes the oscillator to be turned off and the processor to ‘sleep’ until
an external interrupt (IRQ), a low voltage interrupt (LVI), a custom periodic interrupt (CPI), or a
keyboard interrupt occurs, or the device is reset.
WAIT: The WAIT instruction causes all processor clocks to stop, but leaves the timer clocks
running. This ‘rest’ state of the processor can be cleared by reset, an external interrupt (IRQ), a
keyboard interrupt, a timer interrupt (core or 16-bit), or a CPI, SPI, SCI, LVI interrupt. There are no
special WAIT vectors for these interrupts.
MOTOROLA
14-8
2-1.
Custom periodic interrupt (CPI)
Hardware controlled interrupt sequence
RESETS AND INTERRUPTS
MC68HC05F32
TPG
Related parts for XC68HC705F32
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola, Inc [VOLTAGE REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
3N2046367254 MOTOROLA SC (XSTRS/R F)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MOTOROLA POWERPC 603e MICROPROCESSOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola Semiconductor Datasheet Library
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifier(POWERTAP III Package)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifirer
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> MTE53N50E
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SCHOTTKY BARRIER RECTIFIER 200 AMPERES 60 VOLT
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN SILICON POWER DARLINGTON TRANSISTOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet: