SAM9RL64 Atmel Corporation, SAM9RL64 Datasheet - Page 77

SAM9RL64
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM9RL64
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.M40800.pdf
(284 pages)
2.SAM9260.pdf
(290 pages)
3.SAM9261.pdf
(248 pages)
4.SAM9R64.pdf
(903 pages)
5.SAM9R64.pdf
(52 pages)
Specifications of SAM9RL64
Flash (kbytes)
0 Kbytes
Pin Count
217
Max. Operating Frequency
240 MHz
Cpu
ARM926
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
118
Ext Interrupts
118
Usb Transceiver
1
Usb Speed
Hi-Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
5
Ssc
2
Sd / Emmc
1
Graphic Lcd
Yes
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
6
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
220
Resistive Touch Screen
Yes
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
64
Self Program Memory
NO
External Bus Interface
1
Dram Memory
sdram
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.08 to 1.32
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
No / Yes
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
3
Input Capture Channels
3
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
No
- M40800 PDF datasheet
- SAM9260 PDF datasheet #2
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet #3
- SAM9R64 PDF datasheet #4
- SAM9R64 PDF datasheet #5
- Current page: 77 of 284
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
3.3.3
ARM DDI 0029G
Internal cycles
Burst type
Word read
Word write
Halfword read
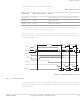
The possible burst types are listed in Table 3-2.
All accesses in a burst are of the same data width, direction, and protection type. For
more details, see Addressing signals on page 3-11.
Memory systems can often respond faster to a sequential access and can require a
shorter access time compared to a nonsequential access. An example of a burst access
is shown in Figure 3-3.
During an internal cycle, the ARM7TDMI processor does not require a memory access,
as an internal function is being performed, and no useful prefetching can be performed
at the same time.
nMREQ
D[31:0]
A[31:0]
MCLK
nRAS
nCAS
SEQ
Copyright © 1994-2001. All rights reserved.
Address increment
4 bytes
4 bytes
2 bytes
N-cycle
Cause
ARM7TDMIcore code fetches, or LDM instruction
STM instruction
Thumb code fetches
a
Figure 3-3 Sequential access cycles
a+4
S-cycle
Table 3-2 Burst types
Memory Interface
a+8
S-cycle
a+12
3-7
Related parts for SAM9RL64
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: