MC68EC000 Motorola, MC68EC000 Datasheet - Page 78

MC68EC000
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68EC000
Description
Core Processor (SCM 68000)
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.MC68EC000.pdf
(145 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA10
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA12
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA16
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA16
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA16R2
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000AA20
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC68EC000CFU10
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000EI10
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
6 239
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000EI16
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
450
Company:
Part Number:
MC68EC000EI16
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
135
A device can use a clock at the same frequency as the system clock, but without a defined
phase relationship to the system clock. This mode of operation is pseudo-asynchronous; it
increases performance by observing timing parameters related to the system clock fre-
quency without being completely synchronous with that clock. A common example of a
pseudo-asynchronous device is a memory array designed to operate with the SCM68000 at
a certain frequency but is not driven by the SCM68000 clock.
The designer of a fully asynchronous system can make no assumptions about address
setup time, which could be used to improve performance. However, with the system clock
frequency known, the slave device can be designed to decode the address bus before rec-
ognizing an address strobe. Parameter #11 (refer to Section 7 Electrical Characteristics
for all parameters listed in this section) specifies the minimum time before address strobe
during which the address is valid.
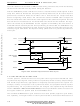
In a pseudo-asynchronous system, timing specifications allow DTACKB to be asserted for
a read cycle (see Figure 3-31) before the data from a slave device is valid. The length of
time that DTACKB may precede data is specified as parameter #31 in Figure 3-31. This
parameter must be met to ensure the validity of the data latched into the SCM68000. No
maximum time is specified from the assertion of ASB to the assertion of DTACKB. During
this unlimited time, the SCM68000 inserts wait cycles in one-clock-period increments until
DTACKB is recognized. Figure 3-31 shows the important timing parameters for a pseudo-
asynchronous read cycle.
During a write cycle (see Figure 3-32), after the SCM68000 asserts ASB but before driving
the data bus, the SCM68000 drives RWB to a logic low. Parameter #55 specifies the mini-
MOTOROLA
UDSB and/or LDSB
and DSB
DTACKB
A31–A0
DATA
RWB
ASB
Figure 3-31. Pseudo-Asynchronous Read Cycle
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
17
EC000 CORE PROCESSOR USER’S MANUAL
15
11
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
31
29
28
Bus Operation
13
3-37