SAM9G45 Atmel Corporation, SAM9G45 Datasheet - Page 229

SAM9G45
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM9G45
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.SAM9261.pdf
(248 pages)
2.SAM9261.pdf
(1274 pages)
3.SAM9261.pdf
(43 pages)
4.SAM9G45.pdf
(10 pages)
5.SAM9G45.pdf
(55 pages)
6.SAM9G45.pdf
(1196 pages)
Specifications of SAM9G45
Flash (kbytes)
0 Kbytes
Pin Count
324
Max. Operating Frequency
400 MHz
Cpu
ARM926
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
160
Ext Interrupts
160
Usb Transceiver
3
Usb Speed
Hi-Speed
Usb Interface
Host, Device
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
5
Lin
4
Ssc
2
Ethernet
1
Sd / Emmc
2
Graphic Lcd
Yes
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
Yes
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
440
Resistive Touch Screen
Yes
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
64
Self Program Memory
NO
External Bus Interface
2
Dram Memory
DDR2/LPDDR, SDRAM/LPSDR
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
0.9 to 1.1
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
No/Yes
Timers
6
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
6
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
No
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet #2
- SAM9261 PDF datasheet #3
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #4
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #5
- SAM9G45 PDF datasheet #6
- Current page: 229 of 248
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
Cache
Cache contention
Cache hit
Cache line
Cache line index
Cache lockdown
Cache miss
Cache set
Cache way
CAM
Cast out
ARM DDI0198D
A block of on-chip or off-chip fast access memory locations, situated between the
processor and main memory, used for storing and retrieving copies of often used
instructions and/or data. This is done to greatly reduce the average speed of memory
accesses and so to increase processor performance.
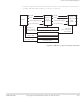
See also Cache terminology diagram on the last page of this glossary.
When the number of frequently-used memory cache lines that use a particular cache set
exceeds the set-associativity of the cache. In this case, main memory activity increases
and performance decreases.
A memory access that can be processed at high speed because the instruction or data
that it addresses is already held in the cache.
The basic unit of storage in a cache. It is always a power of two words in size (usually
four or 8 words), and is required to be aligned to a suitable memory boundary.
See also Cache terminology diagram on the last page of this glossary.
The number associated with each cache line in a cache way. Within each cache way, the
cache lines are numbered from 0 to (set associativity) -1.
See also Cache terminology diagram on the last page of this glossary.
To fix a line in cache memory so that it cannot be overwritten. Cache lockdown enables
critical instructions and/or data to be loaded into the cache so that the cache lines
containing them are not subsequently reallocated. This ensures that all subsequent
accesses to the instructions/data concerned are cache hits, and therefore complete as
quickly as possible.
A memory access that cannot be processed at high speed because the instruction/data it
addresses is not in the cache and a main memory access is required.
A cache set is a group of cache lines (or blocks). A set contains all the ways that can be
addressed with the same index. The number of cache sets is always a power of two.
See also Cache terminology diagram on the last page of this glossary.
A group of cache lines (or blocks). It is 2 to the power of the number of index bits in size.
See also Cache terminology diagram on the last page of this glossary.
See Content Addressable Memory.
See Victim.
Copyright © 2001-2003 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
Glossary-5
Glossary
Related parts for SAM9G45
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: