PIC18F27J53T-I/SO Microchip Technology, PIC18F27J53T-I/SO Datasheet - Page 112

PIC18F27J53T-I/SO
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F27J53T-I/SO
Description
28-pin, USB, 128KB Flash, 4KB RAM, 12 MIPS, 12-bit ADC, NanoWatt XLP 28 SOIC .30
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 18Fr
Specifications of PIC18F27J53T-I/SO
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
48MHz
Connectivity
I²C, LIN, SPI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
22
Program Memory Size
128KB (64K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
3.8K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.15 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 10x10b/12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
*
Processor Series
PIC18F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
3.8 KB
Interface Type
I2C, SPI, USART
Maximum Clock Frequency
48 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
16
Number Of Timers
8
Operating Supply Voltage
2.15 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
- Current page: 112 of 586
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
PIC18F47J53 FAMILY
7.2.2
The Table Latch (TABLAT) is an 8-bit register mapped
into the Special Function Register (SFR) space. The
Table Latch register is used to hold 8-bit data during
data transfers between program memory and data
RAM.
7.2.3
The Table Pointer (TBLPTR) register addresses a byte
within the program memory. The TBLPTR comprises
three SFR registers: Table Pointer Upper Byte, Table
Pointer High Byte and Table Pointer Low Byte
(TBLPTRU:TBLPTRH:TBLPTRL). These three registers
join to form a 22-bit wide pointer. The low-order 21 bits
allow the device to address up to 2 Mbytes of program
memory space. The 22
ID, the user ID and the Configuration bits.
The Table Pointer register, TBLPTR, is used by the
TBLRD and TBLWT instructions. These instructions can
update the TBLPTR in one of four ways based on the
table operation.
Table 7-1 provides these operations. These operations
on the TBLPTR only affect the low-order 21 bits.
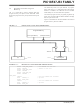
TABLE 7-1:
FIGURE 7-3:
DS39964B-page 112
TBLRD*
TBLWT*
TBLRD*+
TBLWT*+
TBLRD*-
TBLWT*-
TBLRD+*
TBLWT+*
Example
21
TABLE LATCH REGISTER (TABLAT)
TABLE POINTER REGISTER
(TBLPTR)
TABLE POINTER OPERATIONS WITH TBLRD AND TBLWT INSTRUCTIONS
TBLPTRU
nd
TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES BASED ON OPERATION
ERASE: TBLPTR<20:10>
bit allows access to the device
16
15
TABLE WRITE: TBLPTR<20:6>
TBLPTR is incremented before the read/write
TBLPTR is decremented after the read/write
TBLPTR is incremented after the read/write
TABLE READ: TBLPTR<21:0>
TBLPTRH
Preliminary
Operation on Table Pointer
TBLPTR is not modified
registers is written to. When the timed write to program
7.2.4
TBLPTR is used in reads, writes and erases of the
Flash program memory.
When a TBLRD is executed, all 22 bits of the TBLPTR
determine which byte is read from program memory
into TABLAT.
When a TBLWT is executed, the seven Least Significant
bits (LSbs) of the Table Pointer register (TBLPTR<6:0>)
determine which of the 64 program memory holding
memory begins (via the WR bit), the 12 Most Significant
bits (MSbs) of the TBLPTR (TBLPTR<21:10>)
determine which program memory block of 1024 bytes
is written to. For more information, see Section 7.5
“Writing to Flash Program Memory”.
When an erase of program memory is executed, the
12 MSbs of the Table Pointer register point to the
1024-byte block that will be erased. The LSbs are
ignored.
Figure 7-3 illustrates the relevant boundaries of the
TBLPTR based on Flash program memory operations.
8
7
TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES
TBLPTRL
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
0
Related parts for PIC18F27J53T-I/SO
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: