MC9S08JM60CLH Freescale, MC9S08JM60CLH Datasheet - Page 265

MC9S08JM60CLH
Manufacturer Part Number
MC9S08JM60CLH
Description
Manufacturer
Freescale
Datasheet
1.MC9S08JM60CLH.pdf
(388 pages)
Specifications of MC9S08JM60CLH
Cpu Family
HCS08
Device Core Size
8b
Frequency (max)
24MHz
Interface Type
SCI/SPI
Total Internal Ram Size
4KB
# I/os (max)
51
Number Of Timers - General Purpose
8
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3.3/5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
On-chip Adc
12-chx12-bit
Instruction Set Architecture
CISC
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
64
Package Type
LQFP
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
60KB
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC9S08JM60CLH
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC9S08JM60CLH
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC9S08JM60CLHE
Manufacturer:
AZBIL
Quantity:
1 000
- Current page: 265 of 388
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
15.4.9.3
Stop3 mode is dependent on the SPI system. Upon entry to stop3 mode, the SPI module clock is disabled
(held high or low). If the SPI is in master mode and exchanging data when the CPU enters stop mode, the
transmission is frozen until the CPU exits stop mode. After stop, data to and from the external SPI is
exchanged correctly. In slave mode, the SPI will stay synchronized with the master.
The stop mode is not dependent on the SPISWAI bit.
In all other stop modes, the SPI module is completely disabled. After stop, all registers are reset to their
default values, and the SPI module must be re-initialized.
15.4.9.4
The reset values of registers and signals are described in
the registers and their bit-fields.
15.4.9.5
The SPI only originates interrupt requests when the SPI is enabled (SPE bit in SPIxC1 set). The following
is a description of how the SPI makes a request and how the MCU should acknowledge that request. The
interrupt vector offset and interrupt priority are chip dependent.
15.4.10 SPI Interrupts
There are four flag bits, three interrupt mask bits, and one interrupt vector associated with the SPI system.
The SPI interrupt enable mask (SPIE) enables interrupts from the SPI receiver full flag (SPRF) and mode
fault flag (MODF). The SPI transmit interrupt enable mask (SPTIE) enables interrupts from the SPI
transmit buffer empty flag (SPTEF). The SPI match interrupt enable mask bit (SPIMIE) enables interrupts
from the SPI match flag (SPMF). When one of the flag bits is set, and the associated interrupt mask bit is
set, a hardware interrupt request is sent to the CPU. If the interrupt mask bits are cleared, software can poll
the associated flag bits instead of using interrupts. The SPI interrupt service routine (ISR) should check
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
If a data transmission occurs in slave mode after reset without a write to SPIxDH:SPIxDL, it will
transmit garbage, or the data last received from the master before the reset.
Reading from the SPIxDH:SPIxDL after reset will always read zeros.
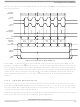
SPI in Stop Mode
Reset
Interrupts
Care must be taken when expecting data from a master while the slave is in
wait or stop3 mode. Even though the shift register will continue to operate,
the rest of the SPI is shut down (i.e. a SPRF interrupt will not be generated
until exiting stop or wait mode). Also, the data from the shift register will
not be copied into the SPIxDH:SPIxDL registers until after the slave SPI has
exited wait or stop mode. A SPRF flag and SPIxDH:SPIxDL copy is only
generated if wait mode is entered or exited during a tranmission. If the slave
enters wait mode in idle mode and exits wait mode in idle mode, neither a
SPRF nor a SPIxDH:SPIxDL copy will occur.
MC9S08JM60 Series Data Sheet, Rev. 3
NOTE
Section 15.3, “Register
Serial Peripheral Interface (S08SPI16V1)
Definition.” which details
265
Related parts for MC9S08JM60CLH
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER ELEVATOR BOARDS HARDWARE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER SERIAL I/O HARDWARE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
LCD MODULE FOR TWR SYSTEM
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DAUGHTER LCD WVGA I.MX51
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER SYSTEM BOARD MPC5125
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT EVALUATION I.MX51
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEVELOPMENT WINCE IMX25
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER SYSTEM KIT MPC5125
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER SYSTEM BOARD K40X256
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TOWER SYSTEM KIT K40X256
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) MX28 PLATFORM DEV KIT
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU, MPU & DSP Development Tools IAR KickStart Kit for Kinetis K60
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
24BIT HDMI MX535/08
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: