ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU Atmel, ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU Datasheet - Page 381
ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU
Description
IC AVR MCU 2.4GHZ XCEIVER 64QFN
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
ATMEGAr
Datasheets
1.ATMEGA128-16AU.pdf
(385 pages)
2.ATAVR128RFA1-EK1.pdf
(13 pages)
3.ATAVR128RFA1-EK1.pdf
(555 pages)
4.ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU.pdf
(524 pages)
Specifications of ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU
Frequency
2.4GHz
Data Rate - Maximum
2Mbps
Modulation Or Protocol
802.15.4 Zigbee
Applications
General Purpose
Power - Output
3.5dBm
Sensitivity
-100dBm
Voltage - Supply
1.8 V ~ 3.6 V
Current - Receiving
12.5mA
Current - Transmitting
14.5mA
Data Interface
PCB, Surface Mount
Memory Size
128kB Flash, 4kB EEPROM, 16kB RAM
Antenna Connector
PCB, Surface Mount
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-VFQFN, Exposed Pad
Rf Ic Case Style
QFN
No. Of Pins
64
Supply Voltage Range
1.8V To 3.6V
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To +85°C
Svhc
No SVHC (15-Dec-2010)
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Processor Series
ATMEGA128x
Core
AVR8
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
128 KB
Data Ram Size
16 KB
Interface Type
JTAG
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
38
Number Of Timers
6
Operating Supply Voltage
1.8 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
EWAVR, EWAVR-BL
Development Tools By Supplier
ATAVR128RFA1-EK1
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA128RFA1-ZUR
Manufacturer:
ON
Quantity:
56 000
- ATMEGA128-16AU PDF datasheet
- ATAVR128RFA1-EK1 PDF datasheet #2
- ATAVR128RFA1-EK1 PDF datasheet #3
- ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU PDF datasheet #4
- Current page: 381 of 524
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
8266A-MCU Wireless-12/09
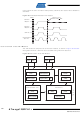
• An algorithm must be implemented allowing only one of the masters to complete the
• Different masters may use different SCL frequencies. A scheme must be devised to
The wired-ANDing of the bus lines is used to solve both these problems. The serial
clocks from all masters will be wired-ANDed, yielding a combined clock with a high
period equal to the one from the Master with the shortest high period. The low period of
the combined clock is equal to the low period of the Master with the longest low period.
Note that all masters listen to the SCL line, effectively starting to count their SCL high
and low time-out periods when the combined SCL line goes high or low, respectively.
Figure 25-7. SCL Synchronization Between Multiple Masters
Arbitration is carried out by all masters continuously monitoring the SDA line after
outputting data. If the value read from the SDA line does not match the value the
Master had output, it has lost the arbitration. Note that a Master can only lose arbitration
when it outputs a high SDA value while another Master outputs a low value. The losing
Master should immediately go to Slave mode, checking if it is being addressed by the
winning Master. The SDA line should be left high, but losing masters are allowed to
generate a clock signal until the end of the current data or address packet. Arbitration
will continue until only one Master remains, and this may take many bits. If several
masters are trying to address the same Slave, arbitration will continue into the data
packet.
Note that arbitration is not allowed between:
• A REPEATED START condition and a data bit.
• A STOP condition and a data bit.
• A REPEATED START and a STOP condition.
It is the user software’s responsibility to ensure that these illegal arbitration conditions
never occur. This implies that in multi-master systems, all data transfers must use the
same composition of SLA+R/W and data packets. In other words: All transmissions
SCL from
SCL from
Master A
Master B
SCL Bus
Line
transmission. All other masters should cease transmission when they discover that
they have lost the selection process. This selection process is called arbitration.
When a contending master discovers that it has lost the arbitration process, it should
immediately switch to Slave mode to check whether it is being addressed by the
winning master. The fact that multiple masters have started transmission at the
same time should not be detectable to the slaves, i.e. the data being transferred on
the bus must not be corrupted.
synchronize the serial clocks from all masters, in order to let the transmission
proceed in a lockstep fashion. This will facilitate the arbitration process.
TA
Counting Low Period
low
Masters Start
TB
low
TA
Counting High Period
high
Masters Start
TB
high
ATmega128RFA1
381
Related parts for ATMEGA128RFA1-ZU
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller with 128K bytes In-system programmable flash, 8 MHz, power supply =2.7 - 5.5V
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 5V 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 5V 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ COM 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ IND 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: