SAM3X8E Atmel Corporation, SAM3X8E Datasheet - Page 547

SAM3X8E
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM3X8E
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
- Current page: 547 of 1465
- Download datasheet (26Mb)
28.2.11
28.2.12
11057A–ATARM–17-Feb-12
11057A–ATARM–17-Feb-12
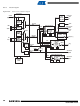
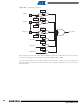
Main Crystal Clock Failure Detector
Programming Sequence
The clock failure detector monitors the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal or Ceramic Resonator-based oscilla-
tor to identify an eventual defect of this oscillator (for example, if the crystal is unconnected).
The clock failure detector can be enabled or disabled by means of the CFDEN bit in the PMC
Clock Generator Main Oscillator Register (CKGR_MOR). After reset, the detector is disabled.
However, if the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal or Ceramic Resonator-based Oscillator is disabled, the
clock failure detector is disabled too.
A failure is detected by means of a counter incrementing on the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal oscillator or
Ceramic Resonator-based oscillator clock edge and timing logic clocked on the slow clock RC
oscillator controlling the counter. The counter is cleared when the slow clock RC oscillator signal
is low and enabled when the slow clock RC oscillator is high. Thus the failure detection time is 1
slow clock RC oscillator clock period. If, during the high level period of the slow clock RC oscilla-
tor, less than 8 fast crystal oscillator clock periods have been counted, then a failure is declared.
If a failure of the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal or Ceramic Resonator-based oscillator clock is detected,
the CFDEV flag is set in the PMC Status Register (PMC_SR), and generates an interrupt if it is
not masked. The interrupt remains active until a read operation in the PMC_SR register. The
user can know the status of the clock failure detector at any time by reading the CFDS bit in the
PMC_SR register.
If the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal or Ceramic Resonator-based oscillator clock is selected as the source
clock of MAINCK (MOSCSEL = 1), and if the Master Clock Source is PLLACK or UPLLCK (CSS
= 2 or 3), a clock failure detection automatically forces MAINCK to be the source clock for the
master clock (MCK).Then, regardless of the PMC configuration, a clock failure detection auto-
matically forces the 4/8/12 MHz Fast RC oscillator to be the source clock for MAINCK. If the Fast
RC oscillator is disabled when a clock failure detection occurs, it is automatically re-enabled by
the clock failure detection mechanism.
It takes 2 slow clock RC oscillator cycles to detect and switch from the 3 to 20 MHz Crystal, or
Ceramic Resonator-based oscillator, to the 4/8/12 MHz Fast RC Oscillator if the Master Clock
source is Main Clock, or 3 slow clock RC oscillator cycles if the Master Clock source is PLLACK
or UPLLCK.
A clock failure detection activates a fault output that is connected to the Pulse Width Modulator
(PWM) Controller. With this connection, the PWM controller is able to force its outputs and to
protect the driven device, if a clock failure is detected. This fault output remains active until the
defect is detected and until it is cleared by the bit FOCLR in the PMC Fault Output Clear Regis-
ter (PMC_FOCR).
The user can know the status of the fault output at any time by reading the FOS bit in the
PMC_SR register.
1. Enabling the Main Oscillator:
The main oscillator is enabled by setting the MOSCXTEN field in the Main Oscillator Regis-
ter (CKGR_MOR). The user can define a start-up time. This can be achieved by writing a
value in the MOSCXTST field in CKGR_MOR. Once this register has been correctly config-
ured, the user must wait for MOSCXTS field in the PMC_SR register to be set. This can be
done either by polling the status register, or by waiting the interrupt line to be raised if the
associated interrupt to MOSCXTS has been enabled in the PMC_IER register.
SAM3X/A
SAM3X/A
547
547
Related parts for SAM3X8E
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: