SAM4S16C Atmel Corporation, SAM4S16C Datasheet - Page 486

SAM4S16C
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM4S16C
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of SAM4S16C
Flash (kbytes)
1024 Kbytes
Pin Count
100
# Of Touch Channels
32
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
79
Ext Interrupts
79
Usb Transceiver
1
Quadrature Decoder Channels
2
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
4
Ssc
1
Sd / Emmc
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
16
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
1000
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Dac Channels
2
Dac Resolution (bits)
12
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
128
Self Program Memory
YES
External Bus Interface
1
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.62 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
Yes / No
Timers
6
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
6
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- Current page: 486 of 1166
- Download datasheet (28Mb)
26.2.8
26.2.9
26.2.10
486
486
SAM4S
SAM4S
Peripheral Clock Controller
Free Running Processor Clock
Programmable Clock Output Controller
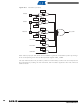
Figure 26-7. USB Clock Controller
The Power Management Controller controls the clocks of each embedded peripheral by means
of the Peripheral Clock Controller. The user can individually enable and disable the Clock on the
peripherals.
The user can also enable and disable these clocks by writing Peripheral Clock Enable 0
(PMC_PCER0), Peripheral Clock Disable 0 (PMC_PCDR0), Peripheral Clock Enable 1
(PMC_PCER1) and Peripheral Clock Disable 1 (PMC_PCDR1) registers. The status of the
peripheral clock activity can be read in the Peripheral Clock Status Register (PMC_PCSR0) and
Peripheral Clock Status Register (PMC_PCSR1).
When a peripheral clock is disabled, the clock is immediately stopped. The peripheral clocks are
automatically disabled after a reset.
In order to stop a peripheral, it is recommended that the system software wait until the peripheral
has executed its last programmed operation before disabling the clock. This is to avoid data cor-
ruption or erroneous behavior of the system.
The bit number within the Peripheral Clock Control registers (PMC_PCER0-1, PMC_PCDR0-1,
and PMC_PCSR0-1) is the Peripheral Identifier defined at the product level. The bit number cor-
responds to the interrupt source number assigned to the peripheral.
The Free Running Processor Clock (FCLK) used for sampling interrupts and clocking debug
blocks ensures that interrupts can be sampled, and sleep events can be traced, while the pro-
cessor is sleeping. It is connected to Master Clock (MCK).
The PMC controls 3 signals to be output on external pins, PCKx. Each signal can be indepen-
dently programmed via the Programmable Clock Registers (PMC_PCKx).
PCKx can be independently selected between the Slow Clock (SLCK), the Main Clock
(MAINCK), the PLLA Clock (PLLACK), the PLLB Clock (PLLBCK) and the Master Clock (MCK)
by writing the CSS field in PMC_PCKx. Each output signal can also be divided by a power of 2
between 1 and 64 by writing the PRES (Prescaler) field in PMC_PCKx.
Each output signal can be enabled and disabled by writing 1 in the corresponding bit, PCKx of
PMC_SCER and PMC_SCDR, respectively. Status of the active programmable output clocks
are given in the PCKx bits of PMC_SCSR (System Clock Status Register).
Moreover, like the PCK, a status bit in PMC_SR indicates that the Programmable Clock is actu-
ally what has been programmed in the Programmable Clock registers.
Source
Clock
USB
/1,/2,/3,.../16
USBDIV
Divider
UDP
UDP Clock (UDPCK)
11100A–ATARM–28-Oct-11
11100A–ATARM–28-Oct-11
Related parts for SAM4S16C
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: