SAM4S16C Atmel Corporation, SAM4S16C Datasheet - Page 541

SAM4S16C
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM4S16C
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of SAM4S16C
Flash (kbytes)
1024 Kbytes
Pin Count
100
# Of Touch Channels
32
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
79
Ext Interrupts
79
Usb Transceiver
1
Quadrature Decoder Channels
2
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
4
Ssc
1
Sd / Emmc
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
16
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
1000
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Dac Channels
2
Dac Resolution (bits)
12
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
128
Self Program Memory
YES
External Bus Interface
1
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.62 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
Yes / No
Timers
6
Output Compare Channels
6
Input Capture Channels
6
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- Current page: 541 of 1166
- Download datasheet (28Mb)
28.5.4
28.5.5
28.5.6
11100A–ATARM–28-Oct-11
11100A–ATARM–28-Oct-11
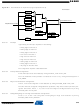
Output Control
Synchronous Data Output
Multi Drive Control (Open Drain)
After reset, PIO_ABCDSR1 and PIO_ABCDSR2 are 0, thus indicating that all the PIO lines are
configured on peripheral A. However, peripheral A generally does not drive the pin as the PIO
Controller resets in I/O line mode.
Writing in PIO_ABCDSR1 and PIO_ABCDSR2 manages the multiplexing regardless of the con-
figuration of the pin. However, assignment of a pin to a peripheral function requires a write in the
peripheral selection registers (PIO_ABCDSR1 and PIO_ABCDSR2) in addition to a write in
PIO_PDR.
When the I/0 line is assigned to a peripheral function, i.e. the corresponding bit in PIO_PSR is at
0, the drive of the I/O line is controlled by the peripheral. Peripheral A or B or C or D depending
on the value in PIO_ABCDSR1 and PIO_ABCDSR2 (ABCD Select Registers) determines
whether the pin is driven or not.
When the I/O line is controlled by the PIO controller, the pin can be configured to be driven. This
is done by writing PIO_OER (Output Enable Register) and PIO_ODR (Output Disable Register).
The results of these write operations are detected in PIO_OSR (Output Status Register). When
a bit in this register is at 0, the corresponding I/O line is used as an input only. When the bit is at
1, the corresponding I/O line is driven by the PIO controller.
The level driven on an I/O line can be determined by writing in PIO_SODR (Set Output Data
Register) and PIO_CODR (Clear Output Data Register). These write operations respectively set
and clear PIO_ODSR (Output Data Status Register), which represents the data driven on the I/O
lines. Writing in PIO_OER and PIO_ODR manages PIO_OSR whether the pin is configured to
be controlled by the PIO controller or assigned to a peripheral function. This enables configura-
tion of the I/O line prior to setting it to be managed by the PIO Controller.
Similarly, writing in PIO_SODR and PIO_CODR effects PIO_ODSR. This is important as it
defines the first level driven on the I/O line.
Clearing one (or more) PIO line(s) and setting another one (or more) PIO line(s) synchronously
cannot be done by using PIO_SODR and PIO_CODR registers. It requires two successive write
operations into two different registers. To overcome this, the PIO Controller offers a direct con-
trol of PIO outputs by single write access to PIO_ODSR (Output Data Status Register).Only bits
unmasked by PIO_OWSR (Output Write Status Register) are written. The mask bits in
PIO_OWSR are set by writing to PIO_OWER (Output Write Enable Register) and cleared by
writing to PIO_OWDR (Output Write Disable Register).
After reset, the synchronous data output is disabled on all the I/O lines as PIO_OWSR resets at
0x0.
Each I/O can be independently programmed in Open Drain by using the Multi Drive feature. This
feature permits several drivers to be connected on the I/O line which is driven low only by each
device. An external pull-up resistor (or enabling of the internal one) is generally required to guar-
antee a high level on the line.
The Multi Drive feature is controlled by PIO_MDER (Multi-driver Enable Register) and
PIO_MDDR (Multi-driver Disable Register). The Multi Drive can be selected whether the I/O line
is controlled by the PIO controller or assigned to a peripheral function. PIO_MDSR (Multi-driver
Status Register) indicates the pins that are configured to support external drivers.
SAM4S
SAM4S
541
541
Related parts for SAM4S16C
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: