MM912H634CV1AE Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634CV1AE Datasheet - Page 189
MM912H634CV1AE
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634CV1AE
Description
64KS12 LIN2xLS/HS Isense
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
-r
Datasheet
1.MM912G634CM1AE.pdf
(345 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634CV1AE
Applications
Automotive
Core Processor
HCS12
Program Memory Type
FLASH (64 kB)
Controller Series
HCS12
Ram Size
6K x 8
Interface
LIN
Number Of I /o
-
Voltage - Supply
5.5 V ~ 27 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 105°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
48-LQFP Exposed Pad
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 189 of 345
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
For hardware data read commands, the external host must wait at least 150 bus clock cycles after sending the address before
attempting to obtain the read data. This is to be certain that valid data is available in the BDM shift register, ready to be shifted
out. For hardware write commands, the external host must wait 150 bus clock cycles after sending the data to be written before
attempting to send a new command. This is to avoid disturbing the BDM shift register before the write has been completed. The
150 bus clock cycle delay in both cases includes the maximum 128 cycle delay that can be incurred as the BDM waits for a free
cycle before stealing a cycle.
For BDM firmware read commands, the external host should wait at least 48 bus clock cycles after sending the command opcode
and before attempting to obtain the read data. The 48 cycle wait allows enough time for the requested data to be made available
in the BDM shift register, ready to be shifted out.
For BDM firmware write commands, the external host must wait 36 bus clock cycles after sending the data to be written before
attempting to send a new command. This is to avoid disturbing the BDM shift register before the write has been completed.
The external host should wait for at least for 76 bus clock cycles after a TRACE1 or GO command before starting any new serial
command. This is to allow the CPU to exit gracefully from the standard BDM firmware lookup table and resume execution of the
user code. Disturbing the BDM shift register prematurely may adversely affect the exit from the standard BDM firmware lookup
table.
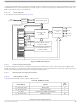
Figure 57
edge. The bar across the top of the blocks indicates that the BKGD line idles in the high state. The time for an 8-bit command is
8 16 target clock cycles.
Note:
Freescale Semiconductor
172.
Target clock cycles are cycles measured using the target MCU’s serial clock rate. See
Section 4.31.3.2.1, “BDM Status Register (BDMSTS)”
Hardware
Hardware
Firmware
Firmware
TRACE
Read
Read
Write
Write
represents the BDM command structure. The command blocks illustrate a series of eight bit times starting with a falling
GO,
16-bit misaligned reads and writes are generally not allowed. If attempted by BDM hardware
command, the BDM ignores the least significant bit of the address and assumes an even
address from the remaining bits.
If the bus rate of the target processor is unknown or could be changing, it is recommended
that the ACK (acknowledge function) is used to indicate when an operation is complete.
When using ACK, the delay times are automated.
AT ~16 TC/Bit
Command
Command
Command
Command
Command
8 Bits
(172)
DELAY
48-BC
76-BC
Delay
AT ~16 TC/Bit
Address
Address
16 Bits
Data
Figure 57. BDM Command Structure
MM912_634 Advance Information, Rev. 4.0
Command
Next
Data
for information on how serial clock rate is selected.
DELAY
36-BC
NOTE
150-BC
Delay
Command
Command
Next
Next
Data
AT ~16 TC/Bit
Section 4.31.4.6, “BDM Serial Interface”
16 Bits
Data
BC = Bus Clock Cycles
TC = Target Clock Cycles
150-BC
Delay
Command
Command
Next
Next
and
189
Related parts for MM912H634CV1AE
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: