MM912H634CV1AE Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634CV1AE Datasheet - Page 233
MM912H634CV1AE
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634CV1AE
Description
64KS12 LIN2xLS/HS Isense
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
-r
Datasheet
1.MM912G634CM1AE.pdf
(345 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634CV1AE
Applications
Automotive
Core Processor
HCS12
Program Memory Type
FLASH (64 kB)
Controller Series
HCS12
Ram Size
6K x 8
Interface
LIN
Number Of I /o
-
Voltage - Supply
5.5 V ~ 27 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 105°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
48-LQFP Exposed Pad
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 233 of 345
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
4.35.0.1
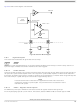
Once the user has programmed the Flash and EEPROM, the chip can be secured by programming the security bits located in
the options/security byte in the Flash memory array. These non-volatile bits will keep the device secured through reset and
power-down.
The options/security byte is located at address 0xFF0F (= global address 0x7F_FF0F) in the Flash memory array. This byte can
be erased and programmed like any other Flash location. Two bits of this byte are used for security (SEC[1:0]). On devices which
have a memory page window, the Flash options/security byte is also available at address 0xBF0F by selecting page 0x3F with
the PPAGE register. The contents of this byte are copied into the Flash security register (FSEC) during a reset sequence.
The meaning of the bits KEYEN[1:0] is shown in
Backdoor Key Access”
The meaning of the security bits SEC[1:0] is shown in
by two bits. To put the device in unsecured mode, these bits must be programmed to SEC[1:0] = ‘10’. All other combinations put
the device in a secured mode. The recommended value to put the device in secured state is the inverse of the unsecured state,
i.e. SEC[1:0] = ‘01’.
4.35.0.2
By securing the device, unauthorized access to the EEPROM and Flash memory contents can be prevented. However, it must
be understood that the security of the EEPROM and Flash memory contents also depends on the design of the application
program. For example, if the application has the capability of downloading code through a serial port and then executing that
code (e.g. an application containing bootloader code), then this capability could potentially be used to read the EEPROM and
Flash memory contents even when the microcontroller is in the secure state. In this example, the security of the application could
be enhanced by requiring a challenge/response authentication before any code can be downloaded.
Secured operation has the following effects on the microcontroller:
4.35.0.2.1
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
•
Background debug module (BDM) operation is completely disabled.
Execution of Flash and EEPROM commands is restricted. Please refer to the NVM block guide for details.
Tracing code execution using the DBG module is disabled.
0xFF0F
Securing the Microcontroller
Operation of the Secured Microcontroller
Please refer to the Flash block guide for actual security configuration (in section “Flash
Module Security”).
Normal Single Chip Mode (NS)
KEYEN1
for more information.
7
KEYEN0
KEYEN[1:0]
SEC[1:0]
6
Table 335. Backdoor Key Access Enable Bits
00
01
10
11
00
01
10
11
Table 334. Flash Options/Security Byte
MM912_634 Advance Information, Rev. 4.0
Table
NV5
5
Table 336. Security Bits
Table
335. Please refer to
336. For security reasons, the state of device security is controlled
NOTE
NV4
4
Access Enabled
Security State
0 (unsecured)
Backdoor Key
NV3
1 (secured)
1 (secured)
1 (secured)
0 (disabled)
0 (disabled)
0 (disabled)
3
1 (enabled)
Section 4.35.0.3.2, “Unsecuring the MCU Using the
NV2
2
SEC1
1
SEC0
0
233
Related parts for MM912H634CV1AE
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: