MM912H634CV1AE Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634CV1AE Datasheet - Page 284
MM912H634CV1AE
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634CV1AE
Description
64KS12 LIN2xLS/HS Isense
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
-r
Datasheet
1.MM912G634CM1AE.pdf
(345 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634CV1AE
Applications
Automotive
Core Processor
HCS12
Program Memory Type
FLASH (64 kB)
Controller Series
HCS12
Ram Size
6K x 8
Interface
LIN
Number Of I /o
-
Voltage - Supply
5.5 V ~ 27 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 105°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
48-LQFP Exposed Pad
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 284 of 345
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
4.39.4
The SPI module allows a duplex, synchronous, serial communication between the MCU and peripheral devices. Software can
poll the SPI status flags or SPI operation can be interrupt driven.
The SPI system is enabled by setting the SPI enable (SPE) bit in SPI control register 1. While SPE is set, the four associated
SPI port pins are dedicated to the SPI function as:
The main element of the SPI system is the SPI data register. The n-bit
register in the slave are linked by the MOSI and MISO pins to form a distributed 2n-bit
operation is performed, this 2n-bit
exchanged between the master and the slave. Data written to the master SPI data register becomes the output data for the slave,
and data read from the master SPI data register after a transfer operation is the input data from the slave.
A read of SPISR with SPTEF = 1 followed by a write to SPIDR puts data into the transmit data register. When a transfer is
complete and SPIF is cleared, received data is moved into the receive data register. This data register acts as the SPI receive
data register for reads and as the SPI transmit data register for writes. A common SPI data register address is shared for reading
data from the read data buffer and for writing data to the transmit data register.
The clock phase control bit (CPHA) and a clock polarity control bit (CPOL) in the SPI control register 1 (SPICR1) select one of
four possible clock formats to be used by the SPI system. The CPOL bit simply selects a non-inverted or inverted clock. The
CPHA bit is used to accommodate two fundamentally different protocols by sampling data on odd numbered SCK edges or on
even numbered SCK edges (see
The SPI can be configured to operate as a master or as a slave. When the MSTR bit in SPI control register1 is set, master mode
is selected, when the MSTR bit is clear, slave mode is selected.
Note:
Freescale Semiconductor
197.
•
•
•
•
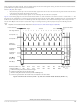
Receive Shift Register
n depends on the selected transfer width, refer to
Slave select (SS)
Serial clock (SCK)
Master out/slave in (MOSI)
Master in/slave out (MISO)
SPI Data Register
Functional Description
A change of CPOL or MSTR bit while there is a received byte pending in the receive shift
register will destroy the received byte and must be avoided.
SPIF
Data A Received
Section 4.39.4.3, “Transmission
(197)
= Unspecified
Figure 106. Reception with SPIF Serviced Too Late
register is serially shifted n
Data A
MM912_634 Advance Information, Rev. 4.0
Section 4.39.3.2.2, “SPI Control Register 2 (SPICR2)
Data A
NOTE
= Reception in progress
Data B Received
(197)
Formats”).
(197)
bit positions by the S-clock from the master, so data is
data register in the master and the n-bit
Data B
(197)
Data B Lost
SPIF Serviced
register. When a data transfer
Data C Received
Data C
Data C
(197)
data
284
Related parts for MM912H634CV1AE
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: