MPC564MZP66 Freescale Semiconductor, MPC564MZP66 Datasheet - Page 513
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC564MZP66
Description
IC MCU 512K FLASH 66MHZ 388-BGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
MPC5xxr
Specifications of MPC564MZP66
Core Processor
PowerPC
Core Size
32-Bit
Speed
66MHz
Connectivity
CAN, EBI/EMI, SCI, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
56
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
32K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 2.7 V
Data Converters
A/D 32x10b
Oscillator Type
External
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Package / Case
388-BGA
For Use With
MPC564EVB - KIT EVAL FOR MPC561/562/563/564
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66R2
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 513 of 1420
- Download datasheet (11Mb)
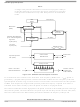
Figure 13-24
counter, clocked at the IMB3 clock rate, is used to create both the high phase and the low phase of the
QCLK signal. At the beginning of the high phase, the 5-bit counter is loaded with the 5-bit PSH value.
When the zero detector finds that the high phase is finished, the QCLK is reset. A 3-bit comparator looks
for a one’s complement match with the 3-bit PSL value, which is the end of the low phase of the QCLK.
The PSA bit was maintained for software compatibility, but has no effect on QADC64E.
The following equations define QCLK frequency:
Where:
The following are equations for calculating the QCLK high/low phases in Example 1:
The following are equations for calculating the QCLK high/low phases in Example 2:
The following are equations for calculating the QCLK high/low phases in Example 3:
Figure 13-25
conversion times based on the following assumption:
Figure 13-25
For other MCU IMB3 clock frequencies and other input sample times, the same calculations can be made.
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
•
•
•
PSH = 0 to 31, the prescaler QCLK high cycles in QACR0
PSL = 0 to 7, the prescaler QCLK low cycles in QACR0
f
FQCLK = QCLK frequency
Input sample time is as fast as possible (IST = 0, 2 QCLK cycles).
SYS
High QCLK Time = (PSH + 1) ÷ f
Low QCLK Time = (PSL + 1) ÷ f
FQCLK= 1 ÷ (High QCLK Time + Low QCLK Time)
High QCLK Time = (19 + 1) ÷ 56 x 10
Low QCLK Time = (7 + 1) ÷ 56 x 10
FQCLK = 1/(357 + 143) = 2 MHz
High QCLK Time = (11 + 1) ÷ 40 x 10
Low QCLK Time = (7 + 1) ÷ 40 x 10
FQCLK = 1/(300 + 200) = 2 MHz
High QCLK Time = (7 + 1) ÷ 32 x 10
Low QCLK Time = (7 + 1) ÷ 32 x 10
FQCLK = 1/(250 + 250) = 2 MHz
= IMB3 clock frequency
and
shows that the prescaler is essentially a variable pulse width signal generator. A 5-bit down
and
The guideline for selecting PSH and PSL is select is to maintain
approximately 50% duty cycle. So for prescaler values less then 16, or PSH
~= PSL. For prescaler values greater than 16 keep PSL as large as possible.
Table 13-21
Table 13-21
also show the conversion time calculated for a single conversion in a queue.
show examples of QCLK programmability. The examples include
MPC561/MPC563 Reference Manual, Rev. 1.2
SYS
SYS
6
6
6
NOTE
6
6
= 200 ns
= 250 ns
= 143 ns
6
= 250 ns
= 300 ns
= 357 ns
QADC64E Legacy Mode Operation
13-49
Related parts for MPC564MZP66
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1K0 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 500R 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5K0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 50K 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: