MPC564MZP66 Freescale Semiconductor, MPC564MZP66 Datasheet - Page 938
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC564MZP66
Description
IC MCU 512K FLASH 66MHZ 388-BGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
MPC5xxr
Specifications of MPC564MZP66
Core Processor
PowerPC
Core Size
32-Bit
Speed
66MHz
Connectivity
CAN, EBI/EMI, SCI, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
56
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
32K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 2.7 V
Data Converters
A/D 32x10b
Oscillator Type
External
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Package / Case
388-BGA
For Use With
MPC564EVB - KIT EVAL FOR MPC561/562/563/564
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66R2
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 938 of 1420
- Download datasheet (11Mb)
Development Support
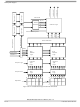
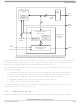
The debug interface is enabled by:
or
The state of this pin is sampled three clocks before the negation of SRESET.
If the DSCK pin is sampled negated, debug mode is disabled until a subsequent reset when the DSCK pin
is sampled in the asserted state. When debug mode is disabled the internal watchpoint/breakpoint hardware
will still be operational and may be used by a software monitor program for debugging purposes.
When debug mode is disabled, all development support registers (see list in
the supervisor code (MSR[PR] = 0) and can be used by a monitor debugger software. However, the
processor never enters debug mode and, therefore, the exception cause register (ECR) and the debug
enable register (DER) are used only for asserting and negating the freeze signal. For more information on
the software monitor debugger support refer to
When debug mode is enabled, all development support registers are accessible only when the CPU is in
debug mode. Therefore, even supervisor code that may be still under debug cannot prevent the CPU from
entering debug mode. The development system has full control of all development support features of the
CPU through the development port. Refer to
23.3.1.2
Entering debug mode can be a result of a number of events. All events have a programmable enable bit to
selectively decide which events result in debug mode entry and which in regular interrupt handling.
23-24
•
•
JCOMP/RSTI
PORESET
Configuration
holding JCOMP/RSTI low while HRESET is asserted and then entering BDM (DSCK=high at
HRESET negation)
configuring READI to be disabled (EVTI=high at RSTI negation) and then entering BDM
(DSCK=high at HRESET negation)
Entering Debug Mode
Because SRESET negation is done by an external pull up resistor any
reference here to SRESET negation time refers to the time the
MPC561/MPC563 releases SRESET. If the actual negation is slow due to a
large resistor, set up time for the debug port signals should be set
accordingly.
(Low)
JTAG disabled
MPC561/MPC563 Reference Manual, Rev. 1.2
Figure 23-7. BDM Mode Selection
Table
READI Disabled/ BDM can be enabled/entered
Section 23.5, “Software Monitor Debugger
NOTE
23-16.
Table
23-14) are accessible to
Freescale Semiconductor
T
Support.”
Related parts for MPC564MZP66
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1K0 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 500R 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5K0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 50K 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: