SAM9G10 Atmel Corporation, SAM9G10 Datasheet - Page 42

SAM9G10
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM9G10
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.SAM9261.pdf
(1274 pages)
2.SAM9261.pdf
(43 pages)
3.SAM9G10.pdf
(750 pages)
4.SAM9G10.pdf
(39 pages)
Specifications of SAM9G10
Flash (kbytes)
0 Kbytes
Pin Count
217
Max. Operating Frequency
266 MHz
Cpu
ARM926
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
96
Ext Interrupts
96
Usb Transceiver
3
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Host, Device
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
4
Ssc
3
Sd / Emmc
1
Graphic Lcd
Yes
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
16
Self Program Memory
NO
External Bus Interface
1
Dram Memory
sdram
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.08 to 1.32
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
No/Yes
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
3
Input Capture Channels
3
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
No
- Current page: 42 of 1274
- Download datasheet (30Mb)
9.6
9.6.1
9.6.2
42
42
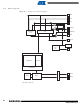
Memory Management Unit (MMU)
SAM9G35
SAM9G35
Access Control Logic
Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB)
The ARM926EJ-S processor implements an enhanced ARM architecture v5 MMU to provide vir-
tual memory features required by operating systems like Symbian OS, WindowsCE, and Linux.
These virtual memory features are memory access permission controls and virtual to physical
address translations.
The Virtual Address generated by the CPU core is converted to a Modified Virtual Address
(MVA) by the FCSE (Fast Context Switch Extension) using the value in CP15 register13. The
MMU translates modified virtual addresses to physical addresses by using a single, two-level
page table set stored in physical memory. Each entry in the set contains the access permissions
and the physical address that correspond to the virtual address.
The first level translation tables contain 4096 entries indexed by bits [31:20] of the MVA. These
entries contain a pointer to either a 1 MB section of physical memory along with attribute infor-
mation (access permissions, domain, etc.) or an entry in the second level translation tables;
coarse table and fine table.
The second level translation tables contain two subtables, coarse table and fine table. An entry
in the coarse table contains a pointer to both large pages and small pages along with access
permissions. An entry in the fine table contains a pointer to large, small and tiny pages.
Table 7 shows the different attributes of each page in the physical memory.
Table 9-6.
The MMU consists of:
The access control logic controls access information for every entry in the translation table. The
access control logic checks two pieces of access information: domain and access permissions.
The domain is the primary access control mechanism for a memory region; there are 16 of them.
It defines the conditions necessary for an access to proceed. The domain determines whether
the access permissions are used to qualify the access or whether they should be ignored.
The second access control mechanism is access permissions that are defined for sections and
for large, small and tiny pages. Sections and tiny pages have a single set of access permissions
whereas large and small pages can be associated with 4 sets of access permissions, one for
each subpage (quarter of a page).
The Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB) caches translated entries and thus avoids going
through the translation process every time. When the TLB contains an entry for the MVA (Modi-
Mapping Name
Section
Large Page
Small Page
Tiny Page
• Access control logic
• Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB)
• Translation table walk hardware
Mapping Details
Mapping Size
1M byte
64K bytes
4K bytes
1K byte
Access Permission By
4 separated subpages
Section
4 separated subpages
Tiny Page
Subpage Size
-
16K bytes
1K byte
-
11053B–ATARM–22-Sep-11
11053B–ATARM–22-Sep-11
Related parts for SAM9G10
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: