M30245FCGP#U1 Renesas Electronics America, M30245FCGP#U1 Datasheet - Page 109

M30245FCGP#U1
Manufacturer Part Number
M30245FCGP#U1
Description
IC M16C/24 MCU FLSH 128K 100LQFP
Manufacturer
Renesas Electronics America
Series
M16C™ M16C/20r
Datasheet
1.M30245FCGPU1.pdf
(268 pages)
Specifications of M30245FCGP#U1
Core Processor
M16C/60
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, SSI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
DMA, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
82
Program Memory Size
128KB (128K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
10K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-20°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
100-LQFP
Package
100LQFP
Family Name
R8C
Maximum Speed
16 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3 V
Data Bus Width
16 Bit
Number Of Programmable I/os
82
Interface Type
USB/UART/I2C/SPI
On-chip Adc
8-chx10-bit
Number Of Timers
5
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
- Current page: 109 of 268
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
M30245 Group
Rev.2.00
REJ03B0005-0200
Transfer cycle
Effect of source and destination addresses
Effect of BYTE pin level
Effect of software wait
Transfer cycle calculations
The transfer cycle consists of the bus cycle in which data is read from memory or from the SFR area (source read) and
the bus cycle in which the data is written to memory or to the SFR area (destination write). The number of read and write
bus cycles depends on the source and destination addresses. In memory expansion mode and microprocessor
mode, the number of read and write bus cycles also depends on the level of the BYTE pin. Also, the bus cycle is longer
when software waits are inserted.
When 16-bit data is transferred on a 16-bit data bus, and the source and destination both start at odd addresses, there
are one more source read cycle and destination write cycle than when the source and destination both start at even
addresses.
When transferring 16-bit data over an 8-bit data bus (BYTE pin = H") in memory expansion mode and microprocessor
mode, the 16 bits of data are sent in two 8-bit blocks. Therefore, two bus cycles are required for reading the data and two
are required for writing the data. Also, in contrast to when the CPU accesses internal memory, when the DMAC
accesses internal memory (internal ROM, internal RAM, and SFR), these areas are accessed using the data size
selected by the BYTE pin.
When the SFR area or a memory area with a software wait is accessed, the number of cycles is increased for the wait
by 1 bus cycle. The length of the cycle is determined by BCLK.
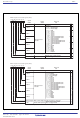
Figure 1.75 shows the example of the transfer cycles for a source read. For convenience, the destination write cycle is
shown as one cycle and the source read cycles for the different conditions are shown. In reality, the destination write
cycle is subject to the same conditions as the source read cycle, with the transfer cycle changing accordingly. When
calculating the transfer cycle, remember to apply the respective conditions to both the destination write cycle and the
source read cycle. For example, if data is being transferred in 16-bit units on an 8-bit bus (2), two bus cycles are required
for both the source read cycle and the destination write cycle.
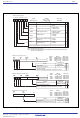
Any combination of even or odd transfer read and write addresses is possible. Table 1.38a shows the number of DMAC
transfer cycles. Table 1.38b shows the Coefficient j,k.
The number of DMAC transfer cycles calculation is:
No. of transfer cycles per transfer unit = No. of read cycles x j + No. of write cycles x k
Oct 16, 2006
page 107 of 264
DMA
Related parts for M30245FCGP#U1
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR M16C/29
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/2D
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
R0K33062P STARTER KIT
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/23 E8A
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C/25
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER H8S2456 SHARPE DSPLY
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C38C
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8C35C
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R8CL3AC+LCD APPS
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR RX610
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR R32C/118
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV RSK-R8C/26-29
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR SH7124
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT STARTER FOR H8SX/1622
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Datasheet: