HD64570 HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor], HD64570 Datasheet - Page 207

HD64570
Manufacturer Part Number
HD64570
Description
Serial Communications Adaptor
Manufacturer
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet
1.HD64570.pdf
(469 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
RENESAS
Quantity:
6 500
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
HIT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP16
Manufacturer:
HIT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP16
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F16
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
HD64570F16
Manufacturer:
HITACHI/日立
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F16V
Manufacturer:
INFINEON
Quantity:
12 000
- Current page: 207 of 469
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
The SYN character pattern is specified by synchronous/address registers 0 and 1 (SA0 and SA1).
To transmit a header preceding the SYN character pattern, write the header pattern to the idle
pattern register (IDL), and delay data write to the transmit buffer. The transmitter keeps
transmitting the header until data is written to the transmit buffer. (For details, see section 5.2.4,
MSCI Control Register (CTL), section 5.2.18, MSCI Synchronous/Address Register 0 (SA0),
section 5.2.19, MSCI Synchronous/Address Register 1 (SA1), and section 5.2.20, MSCI Idle
Pattern Register (IDL).)
The receiver does not reestablish synchronization of the received data using SYN characters in the
data field. The SYN characters in the data field are automatically deleted or loaded into the
receive buffer according to the setting of the SYNCLD bit of CTL. (For details, see section 5.2.4,
MSCI Control Register (CTL).)
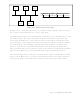
Transmission Operation: Figure 5.24 is the state transition diagram for transmission in byte
synchronous mode.
TX disable state
The transmitter is placed in TX disable state by a hardware reset, a channel reset, or a TX reset
command. It is also placed in TX disable state when no data remains in the transmit buffer
after a TX disable command is issued. In this state, the TXD line is high (mark), and the
TXRDY bit of status register 0 (ST0) is cleared.
Idle state
The TX enable command sets the transmitter in the idle state from the TX disable state. In the
idle state, the transmitter behaves according to the value of the IDLC bit of CTL: a high level
(mark) is transmitted when IDLC is 0, or the contents of IDL are transmitted when IDLC is 1,
via the TXD line. When the transmit data is written, the transmitter enters SYN1 transmit
state.
SYN1 transmit state
The transmitter transmits the SYN character pattern set in SA1, and enters character transmit
state in mono-sync or external synchronous mode, or SYN2 transmit state in bi-sync mode.
(For details, see section 5.2.18, MSCI Synchronous/Address Register 0 (SA0), and section
5.2.19, MSCI Synchronous/Address Register 1 (SA1).)
SYN2 transmit state
When in bi-sync mode, the transmitter transmits the SYN character pattern in SA0 and enters
character transmit state. The transmitter does not enter character transmit state when in mono-
sync or external synchronous mode.
Character transmit state
The transmitter transmits data in FIFO order from the transmit buffer via the TXD line.
CRC transmit state
Rev. 0, 07/98, page 191 of 453
Related parts for HD64570
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
(HD64 Series) Hitachi Single-Chip Microcomputer
Manufacturer:
Hitachi Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
LOW FREQUENCY POWER AMPLIFIER
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON N-CHANNEL JUNCTION FET LOW FREQUECY LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON SPEED POWER SWITCHING
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET HIGH SPEED POWER SWITCHING
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet: