HD64570 HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor], HD64570 Datasheet - Page 239

HD64570
Manufacturer Part Number
HD64570
Description
Serial Communications Adaptor
Manufacturer
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet
1.HD64570.pdf
(469 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
RENESAS
Quantity:
6 500
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
HIT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP16
Manufacturer:
HIT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570CP16
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F16
Manufacturer:
Renesas Electronics America
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
HD64570F16
Manufacturer:
HITACHI/日立
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
HD64570F16V
Manufacturer:
INFINEON
Quantity:
12 000
- Current page: 239 of 469
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
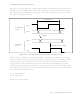
Notes on Clock Extraction: NRZ-type codes differ from FM-type codes in that the data does not
include a clock component. Accordingly, when the ADPLL is used to receive NRZ-type encoded
data by extracting the clock from the data, receive data including a level transition on the RXD
line must be supplied periodically to ensure that the ADPLL does not lose synchronization.
Table 5.18 gives precautions necessary for each type of encoding in each protocol mode.
Table 5.18 Notes on Clock Extraction
Class
NRZ-type
FM-type
t
t
t
Notes: 1. See table 5.16 for the number of transition points needed in the synchronization pattern.
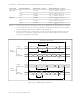
ADPLL Receive Margin: Table 5.19 indicates the theoretical ADPLL receive margin
(the tolerable bit distortion and bit rate distortion).
As shown in figure 5.42, t0 is the width of one bit in the ideal waveform, and it is the width in the
actual waveform. T
Compared with the 8 operating mode, the 32 operating mode samples each bit of input on the
RXD line more often, so the bit margin is higher, but less phase compensation is applied each time
by the ADPLL, so the bit rate margin is lower.
0
1
ADPLL
:
:
:
2. For further information about ADPLL synchronization with an FM-type code, see
Maximum interval containing consecutive 0 data
Maximum interval containing consecutive 1 data
Minimum interval in which ADPLL synchronization can be lost by receiving consecutive
data at the same level.
section 5.4.5, "Notes on Use."
Code
NRZ,
NRZI
FM0,
FM1,
Manch-
ester
0
Protocol Mode Description
Byte
synchronous
mode
Bit
synchronous
mode
Byte
synchronous
mode, bit
synchronous
mode
and T are the ideal and actual time occupied by an arbitrary number of bits.
Ensure that t
transmitting SYN characters, transmit an appropriate
synchronization pattern in the idle state to synchronize the
ADPLL. (See note 1.)
Ensure that t
< t
transmitting an opening flag, transmit an appropriate
synchronization pattern in the idle state to synchronize the
ADPLL. (See note 1.)
In the idle state, have the receiver receive a synchronization
pattern, and issue the enter search mode command to
synchronize the ADPLL. (See note 2.)
ADPLL
(because a flag has six consecutive 1s). Before
0
0
< t
< t
ADPLL
ADPLL
(NRZ only) and t
(NRZ only) and that (6 clock cycles)
Rev. 0, 07/98, page 223 of 453
1
< t
ADPLL
. Before
Related parts for HD64570
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
(HD64 Series) Hitachi Single-Chip Microcomputer
Manufacturer:
Hitachi Semiconductor
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
LOW FREQUENCY POWER AMPLIFIER
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon N-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON N-CHANNEL JUNCTION FET LOW FREQUECY LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON SPEED POWER SWITCHING
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET HIGH SPEED POWER SWITCHING
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SILICON P-CHANNEL MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Silicon P-Channel MOS FET
Manufacturer:
HITACHI [Hitachi Semiconductor]
Datasheet: