ATxmega128B1 Atmel Corporation, ATxmega128B1 Datasheet - Page 241

ATxmega128B1
Manufacturer Part Number
ATxmega128B1
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATxmega128B1
Flash (kbytes)
128 Kbytes
Pin Count
100
Max. Operating Frequency
32 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
53
Ext Interrupts
53
Usb Transceiver
1
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Segment Lcd
160
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
16
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
2000
Analog Comparators
4
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
AES/DES
Sram (kbytes)
8
Eeprom (bytes)
2048
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
Yes
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.6 to 3.6
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.6 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
10
Input Capture Channels
10
Pwm Channels
10
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATxmega128B1-AU
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
90
Company:
Part Number:
ATxmega128B1-U
Manufacturer:
FUJITSU
Quantity:
632
- Current page: 241 of 425
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
19.3.7
8291A–AVR–10/11
Clock and Clock Stretching
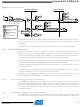
Figure 19-5. Master write transaction.
Assuming the slave acknowledges the address, the master can start transmitting data (DATA)
and the slave will ACK or NACK (A/A) each byte. If no data packets are to be transmitted, the
master terminates the transaction by issuing a STOP condition (P) directly after the address
packet. There are no limitations to the number of data packets that can be transferred. If the
slave signals a NACK to the data, the master must assume that the slave cannot receive any
more data and terminate the transaction.
Figure 19-6 on page 241
action by issuing a START condition followed by an address packet with the direction bit set to
one (ADDRESS+R). The addressed slave must acknowledge the address for the master to be
allowed to continue the transaction.
Figure 19-6. Master read transaction.
Assuming the slave acknowledges the address, the master can start receiving data from the
slave. There are no limitations to the number of data packets that can be transferred. The slave
transmits the data while the master signals ACK or NACK after each data byte. The master ter-
minates the transfer with a NACK before issuing a STOP condition.
Figure 19-7
and write transactions separated by repeated START conditions (Sr).
Figure 19-7. Combined Transaction.
All devices connected to the bus are allowed to stretch the low period of the clock to slow down
the overall clock frequency or to insert wait states while processing data. A device that needs to
stretch the clock can do this by holding/forcing the SCL line low after it detects a low level on the
line.
S
S
S
ADDRESS
Address Packet #1
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
illustrates a combined transaction. A combined transaction consists of several read
Address Packet
Address Packet
R/W
A
Direction
illustrates the master read transaction. The master initiates the trans-
W
R
N Data Packets
DATA
A
A
Transaction
Transaction
A/A
DATA
DATA
Data Packet
Data Packet
Transaction
Sr
ADDRESS
Address Packet #2
Atmel AVR XMEGA B
N data packets
N data packets
A
A
R/W
A
Direction
DATA
DATA
M Data Packets
DATA
A/A
A
A/A
P
P
241
P
Related parts for ATxmega128B1
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: