ATxmega128B1 Atmel Corporation, ATxmega128B1 Datasheet - Page 65

ATxmega128B1
Manufacturer Part Number
ATxmega128B1
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATxmega128B1
Flash (kbytes)
128 Kbytes
Pin Count
100
Max. Operating Frequency
32 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
53
Ext Interrupts
53
Usb Transceiver
1
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Segment Lcd
160
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
16
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
2000
Analog Comparators
4
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
AES/DES
Sram (kbytes)
8
Eeprom (bytes)
2048
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
Yes
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.6 to 3.6
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.6 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
10
Input Capture Channels
10
Pwm Channels
10
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATxmega128B1-AU
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
90
Company:
Part Number:
ATxmega128B1-U
Manufacturer:
FUJITSU
Quantity:
632
- Current page: 65 of 425
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
6. Event System
6.1
6.2
8291A–AVR–10/11
Features
Overview
•
•
•
•
•
•
The event system enables direct peripheral-to-peripheral communication and signaling. It allows
a change in one peripheral’s state to automatically trigger actions in other peripherals. It is
designed to provide a predictable system for short and predictable response times between
peripherals. It allows for autonomous peripheral control and interaction without the use of inter-
rupts or CPU, or DMA controller resources, and is thus a powerful tool for reducing the
complexity, size and execution time of application code. It also allows for synchronized timing of
actions in several peripheral modules.
A change in a peripheral’s state is referred to as an event, and usually corresponds to the
peripheral’s interrupt conditions. Events can be directly passed to other peripherals using a ded-
icated routing network called the event routing network. How events are routed and used by the
peripherals is configured in software.
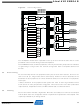
Figure 6-1 on page 65
can directly connect together analog converters, analog comparators, I/O port pins, the real-time
counter, timer/counter and IR communication module (IRCOM), and USB interface. It can also
be used to trigger DMA transactions (DMA controller). Events can also be generated from soft-
ware and the peripheral clock.
Figure 6-1.
System for direct peripheral-to-peripheral communication and signaling
Peripherals can directly send, receive, and react to peripheral events
Four event channels for up to four different and parallel signal routings and configurations
Events can be sent and/or used by most peripherals, clock system, and software
Additional functions include
Works in active mode and idle sleep mode
– CPU and DMA controller independent operation
– 100% predictable signal timing
– Short and guaranteed response time
– Quadrature decoders
– Digital filtering of I/O pin state
Event system overview and connected peripherals.
shows a basic diagram of all connected peripherals. The event system
ADC
AC
Software
Port pins
CPU /
Event Routing Network
Controller
System
Event
Controller
IRCOM
DMA
Atmel AVR XMEGA B
Real Time
Prescaler
Counters
Counter
Timer /
clk
USB
PER
65
Related parts for ATxmega128B1
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: