CS5535-UDCF AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), CS5535-UDCF Datasheet - Page 165

CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer Part Number
CS5535-UDCF
Description
Manufacturer
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet
1.CS5535-UDCF.pdf
(579 pages)
Specifications of CS5535-UDCF
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer:
AMD
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 165 of 579
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
General Purpose Input/Output
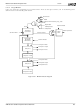
5.15.5.5 Output Steering (Mapping)
Outputs from the internal GPIO circuits, driven by inputs to
the Geode CS5535 companion device from the system,
may be steered (or ‘mapped’) to either interrupts, or power
management events (PME). Sufficient steering logic exists
in the Geode CS5535 companion device to provide for
eight independent interrupts and simultaneously for eight
independent PMEs.
The eight GPIO interrupts are all in Working power domain;
of the eight PMEs, [7:6] are in Standby power domain and
[5:0] are in Working domain. Those in the Standby power
domain are intended to be used to awaken the system
when the Working power domain is off, however, they may
also be used when the Working power domain is on. The
interrupts are connected to the PIC subsystem, and the
PMEs are connected to the Power Management sub-
system.
Four 32-bit steering registers control the routing of the
GPIOs’ internal output (that produced by an input to the
chip from an external source, or from one of the internally-
connected AUX inputs) to either an interrupt or PME. The
set of four registers taken together, contain a nibble for
each GPIO. The upper bit of each nibble selects either a
PME (if high) or an interrupt (if low). The remaining three
bits of each nibble select which of the eight possible inter-
rupts or PMEs the GPIO will be steered to.
The four registers are identified as GPIO Mapper X, Y, Z,
and W. Their GPIO associations are as follows:
• GPIO_MAP_X = GPIO[7:0]
• GPIO_MAP_Y = GPIO[15:8]
• GPIO_MAP_Z = GPIO[23:16]
• GPIO_MAP_W = GPIO[31:24]
The steering logic does not prohibit mapping of two or
more GPIOs to the same output, but it is impossible to cre-
ate a single GPIO that functions simultaneously as both an
interrupt and a PME. Registers X, Y, Z, and W default to all
0s, as do both the High and Low EVNT_EN registers.
Thus, all GPIOs are mapped to INT[0] after a reset, but
none are enabled.
AMD Geode™ CS5535 Companion Device Data Book
5.15.5.6 Auto-sense
Two GPIOs (GPIO5 and GPIO6) have a function called
“Auto-sense”. Auto-sense is a method of automatically
determining whether or not to apply a pull-up or pull-down
to the corresponding GPIO input.
Auto-sensed inputs behave as follows: when reset is
applied to the system, a weak pull-up is applied to the pad.
When reset is de-asserted, the sensed value is used to
establish the pull-up/down state on the de-assertion edge.
If nothing pulls down the pad, then the pull-up continues to
be applied. If the pad is pulled down, then the pull-up is
cleared to 0 and the pull-down is set to 1. If a pull-down is
desired, a diode between the reset signal and the GPIO pin
will pull it down during the auto-sense operation but have
no effect during normal operation.
Disabling the auto-sensed pull-up or pull-down requires
more program operation than just disabling the pull-up or
pull-down through the GPIOL_PU_EN or GPIOL_PD_EN.
If the pullup was enabled through auto-sense, the proce-
dure to disable is:
1)
2)
3)
If the pull-down was enabled through auto-sense, the pro-
cedure to disable is:
1)
2)
3)
Disable the pull-up in GPIOL_PU_EN.
Enable the pull-down in GPIOL_PD_EN.
Disable the pull-down in GPIOL_PD_EN.
Disable the pull-down in GPIOL_PD_EN.
Enable the pull-up in GPIOL_PU_EN.
Disable the pull-up in GPIOL_PU_EN.
31506B
165
Related parts for CS5535-UDCF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6™-2E Embedded Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet: