MM912H634DM1AER2 Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634DM1AER2 Datasheet - Page 101
MM912H634DM1AER2
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634DM1AER2
Description
16-bit Microcontrollers - MCU 64KS12 LIN2XLS/HS ISENSE
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MM912G634DV1AE.pdf
(338 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634DM1AER2
Rohs
yes
Core
HCS12
Processor Series
MM912F634
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Program Memory Size
32 KB
Data Ram Size
2 KB
On-chip Adc
Yes
Operating Supply Voltage
5.5 V to 18 V
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 105 C
Package / Case
LQFP-48
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
A/d Bit Size
10 bit
A/d Channels Available
15
Interface Type
SPI
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Programmable I/os
15
Number Of Timers
1
Program Memory Type
Flash
Supply Voltage - Max
18 V
Supply Voltage - Min
5.5 V
- Current page: 101 of 338
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
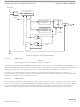
Functional Description and Application Information
Clock A is used as an input to an 8-bit down counter. This down counter loads a user programmable scale value from the scale
register (PWMSCLA). When the down counter reaches one, a pulse is output and the 8-bit counter is re-loaded. The output signal
from this circuit is further divided by two. This gives a greater range with only a slight reduction in granularity. Clock SA equals
clock A divided by two times the value in the PWMSCLA register.
Similarly, clock B is used as an input to an 8-bit down counter followed by a divide by two producing clock SB. Thus, clock SB
equals clock B divided by two times the value in the PWMSCLB register.
As an example, consider the case in which the user writes $FF into the PWMSCLA register. Clock A for this case will be E divided
by 4. A pulse will occur at a rate of once every 255x4 E cycles. Passing this through the divide by two circuit produces a clock
signal at an E divided by 2040 rate. Similarly, a value of $01 in the PWMSCLA register when clock A is E divided by 4 will produce
a clock at an E divided by 8 rate.
Writing to PWMSCLA or PWMSCLB causes the associated 8-bit down counter to be re-loaded. Otherwise, when changing rates
the counter would have to count down to $01 before counting at the proper rate. Forcing the associated counter to re-load the
scale register value every time PWMSCLA or PWMSCLB is written prevents this.
4.13.4.1.3
Each PWM channel has the capability of selecting one of two clocks. For channels 0 the clock choice is clock A or clock SA. For
channels 1 the choice is clock B or clock SB. The clock selection is done with the PCLKx control bits in the PWMCTL register.
4.13.4.2
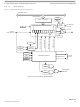
The main part of the PWM module are the actual timers. Each of the timer channels has a counter, a period register, and a duty
register (each are 8-bit). The waveform output period is controlled by a match between the period register and the value in the
counter. The duty is controlled by a match between the duty register and the counter value, and causes the state of the output to
change during the period. The starting polarity of the output is also selectable on a per channel basis. Shown in
block diagram for the PWM timer.
Freescale Semiconductor
PWM Channel Timers
Clock SA = Clock A / (2 * PWMSCLA)
When PWMSCLA = $00, PWMSCLA value is considered a full scale value of 256. Clock A
is thus divided by 512.
Clock SB = Clock B / (2 * PWMSCLB)
When PWMSCLB = $00, PWMSCLB value is considered a full scale value of 256. Clock B
is thus divided by 512.
Writing to the scale registers while channels are operating can cause irregularities in the
PWM outputs.
Clock Select
Changing clock control bits while channels are operating can cause irregularities in the PWM
outputs.
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
PWM Control Module (PWM8B2C)
Figure 26
MM912F634
is the
101
Related parts for MM912H634DM1AER2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: