MM912H634DM1AER2 Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634DM1AER2 Datasheet - Page 327
MM912H634DM1AER2
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634DM1AER2
Description
16-bit Microcontrollers - MCU 64KS12 LIN2XLS/HS ISENSE
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MM912G634DV1AE.pdf
(338 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634DM1AER2
Rohs
yes
Core
HCS12
Processor Series
MM912F634
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Program Memory Size
32 KB
Data Ram Size
2 KB
On-chip Adc
Yes
Operating Supply Voltage
5.5 V to 18 V
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 105 C
Package / Case
LQFP-48
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
A/d Bit Size
10 bit
A/d Channels Available
15
Interface Type
SPI
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Programmable I/os
15
Number Of Timers
1
Program Memory Type
Flash
Supply Voltage - Max
18 V
Supply Voltage - Min
5.5 V
- Current page: 327 of 338
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
Functional Description and Application Information
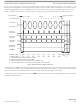
The SS line can remain active low between successive transfers (can be tied low at all times). This format is sometimes preferred
in systems having a single fixed master and a single slave that drive the MISO data line.
The SPI interrupt request flag (SPIF) is common to both the master and slave modes. SPIF gets set one half SCK cycle after the
last SCK edge.
4.38.4.4
Baud rate generation consists of a series of divider stages. Six bits in the SPI baud rate register (SPPR2, SPPR1, SPPR0, SPR2,
SPR1, and SPR0) determine the divisor to the SPI module clock which results in the SPI baud rate.
The SPI clock rate is determined by the product of the value in the baud rate preselection bits (SPPR2–SPPR0) and the value
in the baud rate selection bits (SPR2–SPR0). The module clock divisor equation is shown in
When all bits are clear (the default condition), the SPI module clock is divided by 2. When the selection bits (SPR2–SPR0) are
001 and the preselection bits (SPPR2–SPPR0) are 000, the module clock divisor becomes 4. When the selection bits are 010,
the module clock divisor becomes 8, etc.
Freescale Semiconductor
•
Back-to-back transfers in master mode
In master mode, if a transmission has completed and a new data byte is available in the SPI data register, this byte is
sent out immediately without a trailing and minimum idle time.
End of Idle State
SCK Edge Number
SCK (CPOL = 0)
SCK (CPOL = 1)
SAMPLE I
MOSI/MISO
CHANGE O
CHANGE O
SEL SS (O)
Master only
SEL SS (I)
MOSI pin
MISO pin
t
t
t
L
T
I
MSB first (LSBFE = 0):
LSB first (LSBFE = 1):
= Minimum idling time between transfers (minimum SS high time), not required for back-to-back transfers
SPI Baud Rate Generation
= Minimum leading time before the first SCK edge, not required for back-to-back transfers
= Minimum trailing time after the last SCK edge
For maximum allowed baud rates, refer to
t
L
1
BaudRateDivisor = (SPPR + 1) 2
MSB
LSB
2
Figure 104. SPI Clock Format 1 (CPHA = 1)
3
Begin
Bit 6
Bit 1
4
5
Bit 5
Bit 2
6
7
NOTE
Bit 4
Bit 3
Section 3.6.2.4, “SPI Timing"
8
Transfer
9
Bit 3
Bit 4
10
11
(SPR + 1)
Bit 2
Bit 5
12
13 14
Bit 1
Bit 6
End
Serial Peripheral Interface (S12SPIV4)
15
in this data sheet.
MSB
Equation
LSB
16
t
T
Minimum 1/2 SCK
Begin of Idle State
t
I
for t
4.
T
t
L
, t
l
, t
L
MM912F634
Eqn. 4
327
Related parts for MM912H634DM1AER2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: