MM912H634DM1AER2 Freescale Semiconductor, MM912H634DM1AER2 Datasheet - Page 208
MM912H634DM1AER2
Manufacturer Part Number
MM912H634DM1AER2
Description
16-bit Microcontrollers - MCU 64KS12 LIN2XLS/HS ISENSE
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MM912G634DV1AE.pdf
(338 pages)
Specifications of MM912H634DM1AER2
Rohs
yes
Core
HCS12
Processor Series
MM912F634
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Maximum Clock Frequency
20 MHz
Program Memory Size
32 KB
Data Ram Size
2 KB
On-chip Adc
Yes
Operating Supply Voltage
5.5 V to 18 V
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 105 C
Package / Case
LQFP-48
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
A/d Bit Size
10 bit
A/d Channels Available
15
Interface Type
SPI
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 105 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Number Of Programmable I/os
15
Number Of Timers
1
Program Memory Type
Flash
Supply Voltage - Max
18 V
Supply Voltage - Min
5.5 V
- Current page: 208 of 338
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
Functional Description and Application Information
Figure 66
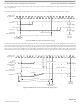
example. First, the 8-bit instruction opcode is sent by the host, followed by the address of the memory location to be read. The
target BDM decodes the instruction. A bus cycle is grabbed (free or stolen) by the BDM and it executes the READ_BYTE
operation. Having retrieved the data, the BDM issues an ACK pulse to the host controller, indicating that the addressed byte is
ready to be retrieved. After detecting the ACK pulse, the host initiates the byte retrieval process. Note that data is sent in the form
of a word and the host needs to determine which is the appropriate byte based on whether the address was odd or even.
Differently from the normal bit transfer (where the host initiates the transmission), the serial interface ACK handshake pulse is
initiated by the target MCU by issuing a negative edge in the BKGD pin. The hardware handshake protocol in
the timing when the BKGD pin is being driven, so the host should follow this timing constraint in order to avoid the risk of an
electrical conflict in the BKGD pin.
Freescale Semiconductor
BKGD Pin
(Target MCU)
BDM Clock
ACK Pulse
BKGD Pin
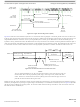
shows the ACK handshake protocol in a command level timing diagram. The READ_BYTE instruction is used as an
Transmits
Last Command Bit
16th Tick of the
Target
READ_BYTE
The only place the BKGD pin can have an electrical conflict is when one side is driving low
and the other side is issuing a speedup pulse (high). Other “highs” are pulled rather than
driven. However, at low rates the time of the speedup pulse can become lengthy and so the
potential conflict time becomes longer as well.
Host
High-impedance
Byte Address
Target
32 Cycles
Figure 66. Handshake Protocol at Command Level
Figure 65. Target Acknowledge Pulse (ACK)
BDM Decodes
the Command
Minimum Delay
From the BDM Command
NOTE
16 Cycles
BDM Executes the
READ_BYTE Command
Speedup Pulse
Target
BDM Issues the
ACK Pulse (out of scale)
(2) Bytes are
Background Debug Module (S12SBDMV1)
Retrieved
Host
Next Bit
Earliest
Start of
High-impedance
Host
Command
New BDM
Figure 65
Target
MM912F634
specifies
208
Related parts for MM912H634DM1AER2
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: