Z0847006PSG Zilog, Z0847006PSG Datasheet - Page 155

Z0847006PSG
Manufacturer Part Number
Z0847006PSG
Description
IC 6MHZ Z80 NMOS DART 40-DIP
Manufacturer
Zilog
Series
Z80r
Datasheet
1.Z0847006PSG.pdf
(330 pages)
Specifications of Z0847006PSG
Processor Type
Z80
Features
Dual Channel Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (DART)
Speed
6MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
40-DIP (0.620", 15.75mm)
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Cpu Speed
6MHz
Digital Ic Case Style
DIP
No. Of Pins
40
Supply Voltage Range
5V
Operating Temperature Range
0°C To +70°C
Svhc
No SVHC (18-Jun-2010)
Base Number
847006
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Clock Frequency
6MHz
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
Z0847006PSG
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Quantity:
22
- Current page: 155 of 330
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
< % 2 7 2 G T K R J G T C N U
7 U G T / C P W C N
(floated) in a manner similar to the CPU and DMA address pins. For
example, in a system with one CPU and one DMA, the BUSACK signal
can disable CPU buffers and enable DMA buffers when it is active. Where
there are three or more potential bus masters, only those buffers associated
with the actual bus master must be active at any time. Therefore, each
DMA, if its BAI signal is active (Low) and its BAO signal is inactive
(High), has control of the bus and can enable its drivers.
Data bus lines are bidirectional, making their buffer control more compli-
cated. Any device from which the CPU can read drives the data bus when it
is selected and the RD control signal is active. In this sense, the RD signal
is the principal directional control. Non-CPU devices also drive the data
bus during interrupt-acknowledge cycles in which the device puts its
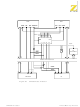
vector on the bus and during DMA write cycles. Figure 54 illustrates a
bidirectional data bus buffer and its control. Here, Z80 SIC, PIO, CTC,
and DMA peripherals share a circuit card. Their common on-card data
bus is buffered to and from the system (motherboard or backplane) bus.
Each of the three conditions mentioned causes the buffers to drive data out
onto the system bus; otherwise, data is buffered into the card. Suitable
devices for bidirectional buffering include the 74LS241 (tristate bus
drivers) and 74LS245 (transceivers).
The control signals MREQ, IORQ, RD, and WR should be unidirectionally
buffered in large- or multi-card systems. These signal buffers are, again,
enabled when their associated device or card has bus control and are forced
into high-impedance states when another master takes control of these bus
lines. Because there are short intervals during transfer of the bus (when the
bus is not driven by any master), MREQ, IORQ, RD, and WR should be
pulled up to + 5V with 2.7 Kohms to 4.7 Kohms resistors so that they
remain inactive. Other control signals on CPU and DMA may be perma-
nently driven. This usually includes M1, RFSH, and HALT from the CPU,
and BAO from a DMA.
The BUSREQ line is bidirectional and cannot easily be externally buffered.
However, the DMA can sink 3.2 mA on BUSREQ, more than on other
UM008101-0601
Direct Memory Access
Related parts for Z0847006PSG
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Customer Procurement Spec(CPS)
Manufacturer:
ZILOG [Zilog, Inc.]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Communication Controllers, ZILOG INTELLIGENT PERIPHERAL CONTROLLER (ZIP)
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV FOR Z8 ENCORE 16K TO 64K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 8K/4K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 4K TO 8K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS Z8 microcontroller. ROM 16 Kbytes, RAM 256 bytes, speed 16 MHz, 32 lines I/O, 3.0V to 5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-cost microcontroller. 512 bytes ROM, 61 bytes RAM, 8 MHz
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Z8 4K OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS SUPER8 ROMLESS MCU
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
OTP (KB) = 1, RAM = 125, Speed = 12, I/O = 14, 8-bit Timers = 2, Comm Interfaces Other Features = Por, LV Protect, Voltage = 4.5-5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet: