Z0847006PSG Zilog, Z0847006PSG Datasheet - Page 165

Z0847006PSG
Manufacturer Part Number
Z0847006PSG
Description
IC 6MHZ Z80 NMOS DART 40-DIP
Manufacturer
Zilog
Series
Z80r
Datasheet
1.Z0847006PSG.pdf
(330 pages)
Specifications of Z0847006PSG
Processor Type
Z80
Features
Dual Channel Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (DART)
Speed
6MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
40-DIP (0.620", 15.75mm)
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Cpu Speed
6MHz
Digital Ic Case Style
DIP
No. Of Pins
40
Supply Voltage Range
5V
Operating Temperature Range
0°C To +70°C
Svhc
No SVHC (18-Jun-2010)
Base Number
847006
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Clock Frequency
6MHz
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
Z0847006PSG
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Quantity:
22
- Current page: 165 of 330
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
< % 2 7 2 G T K R J G T C N U
7 U G T / C P W C N
Non-Z80 interrupt environments do not use the IEI and IEO signals, and
often they use separate interrupt controllers to generate vectors, and handle
acknowledgement and return in different ways, or not at all.
Interrupt request is usually easy: active levels typically are low voltage, and
there may be one or more separate interrupt request pins. Timing require-
ments for interrupt requests are varied and may including pulse widths,
latching, and more, and must be carefully examined.
Priority of simultaneous or overlapping requests is handled in several ways:
some processors (for example, the 8085) have multiple interrupt-request
pins, some use daisy-chained priority schemes (as in the Z80), and several
types of interrupt control ICs are available.
Acknowledgement and identification methods vary too. Sometimes, several
fixed memory locations correspond to different interrupt pins’ service
routines. In other cases, the interrupting device identifies itself by putting a
vector or instruction on the data bus for the CPU to read. Interrupt
controllers often provide appropriate vectors to the CPU and distinguish
between and prioritize multiple requests. The DMA has the built-in capa-
bility of supplying an arbitrary vector byte when it detects a Z80 interrupt
acknowledge (IORQ and M1 both active) and its IEI input is active (no
higher-priority device is interrupting). Often, then, gating the M1, IORQ,
and IEI pins appropriately can rule out using a separate interrupt controller.
IORQ serves another function, too, therefore it must appear during CPU-
DMA transfers and be available to signal I/O reads or writes in the active
state.
At the end of its service routine, the DMA anticipates the CPU fetching the
RETI instruction (ED, 4D present on the data bus accompanied by M1).
The DMA command RESET AND DISABLE INTERRUPTS is designed
for this purpose in non-Z80 CPU environments. Alternatively, the RETI
instruction might be simulated by re-gating M1 and programming the CPU
to write to a phantom peripheral the bytes ED, 4D. The chip select for this
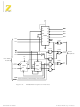
nonexistent peripheral is used to simulate M1. See Figure 57.
UM008101-0601
Direct Memory Access
Related parts for Z0847006PSG
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Customer Procurement Spec(CPS)
Manufacturer:
ZILOG [Zilog, Inc.]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Communication Controllers, ZILOG INTELLIGENT PERIPHERAL CONTROLLER (ZIP)
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV FOR Z8 ENCORE 16K TO 64K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 8K/4K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
KIT DEV Z8 ENCORE XP 28-PIN
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR Z8 ENCORE 4K TO 8K
Manufacturer:
Zilog
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS Z8 microcontroller. ROM 16 Kbytes, RAM 256 bytes, speed 16 MHz, 32 lines I/O, 3.0V to 5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-cost microcontroller. 512 bytes ROM, 61 bytes RAM, 8 MHz
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Z8 4K OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CMOS SUPER8 ROMLESS MCU
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SL1866 CMOSZ8 OTP Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
OTP (KB) = 1, RAM = 125, Speed = 12, I/O = 14, 8-bit Timers = 2, Comm Interfaces Other Features = Por, LV Protect, Voltage = 4.5-5.5V
Manufacturer:
Zilog, Inc.
Datasheet: