NQ5000P S L9TN Intel, NQ5000P S L9TN Datasheet - Page 326

NQ5000P S L9TN
Manufacturer Part Number
NQ5000P S L9TN
Description
Manufacturer
Intel
Datasheet
1.NQ5000P_S_L9TN.pdf
(530 pages)
Specifications of NQ5000P S L9TN
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
- Current page: 326 of 530
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
5.2.13
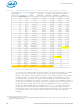
Table 5-11. Electrical Throttle Window as a Function of DIMM Technology
5.3
326
Electrical Throttling
Electrical throttling is a mechanism that limits the number of activates (burstiness)
within a very short time interval that would otherwise cause silent data corruption on
the DIMMs. Electrical throttling is enabled by setting the MTR.ETHROTTLE bit defined in
Section
electrical throttling should be used. It is assumed that both ranks within a DIMM would
be the same technology, and therefore does need not separate enable bits.
The per rank electrical throttling for FB-DIMM is 4 activates per 37.5ns window (JEDEC
consensus) and is summarized in
a. Maximum 4 activates per rank is allowed within the window.
b. This is not a supported technology/nor a POR for Intel 5000P Chipset MCH and is tabulated for
The MC.ETHROT configuration register field limits the number of activations per sliding
electrical throttle window. The memory controller logic can implement the sliding
electrical throttle window with a 20-bit shift register per rank in each DIMM pair per
branch. This register records for the last 20 clocks, whether an activate was issued or
not to that rank. The number of activates can then be summed up from the state of the
shift register and compared with the respective limit as shown in
limit is reached, then further activates to the rank are blocked until the count falls
below the limit. The Electrical throttling logic in the MC masks off the end bits for the
DIMM technologies that require fewer clocks. As an example, if the DIMM technology
used is DDR667, then it can allow 4 activates within the last 13 clocks, the remaining 7
bits are masked (forced to 0) so they do not prevent activates.
Intel 5000P Chipset Behavior on Overtemp State
in AMB
Overtemperature occurring in an AMB may lead to data corruption in the Intel 5000P
Chipset.
Notes:
DIMM Modes
• If EI is received by Intel 5000P Chipset due to Overtemp detection in one of the
• If the EI is interpreted as having both good CRC and good ECC, this could cause
Conservative
(safe mode)
information/illustrative purposes only.
DDR800
DDR533
DDR667
AMBs, Intel 5000P Chipset will capture random data that most likely will be
interpreted as having a CRC or uncorrectable ECC error causing the link to go into a
fast reset loop without data corruption.
data corruption until a bad CRC/ECC frame is detected and the link enters the fast
reset loop.
3.9.23.7. These bits occur on a per DIMM pair basis per branch as to whether
b
Core: FB-DIMM
Chipset MCH
Intel 5000P
clock Ratio
1:1
5:4
1:1
4:5
All
All
Intel® 5000P/5000V/5000Z Chipset Memory Controller Hub (MCH) Datasheet
Electrical Throttle Window
Table 5-11
per DIMM pair per branch)
for various DIMM technologies.
13 (conservative)
13
15
20
10
13
a
(in core clocks per rank
Figure
Functional Description
5-11. If the
Related parts for NQ5000P S L9TN
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
5000P Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microprocessor: Intel Celeron M Processor 320 and Ultra Low Voltage Intel Celeron M Processor at 600MHz
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation

Part Number:
Description:
Intel 82550 Fast Ethernet Multifunction PCI/CardBus Controller
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel StrataFlash memory 32 Mbit. Access speed 120 ns
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel StrataFlash memory 32 Mbit. Access speed 120 ns
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel StrataFlash memory 64 Mbit. Access speed 150 ns
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel StrataFlash memory 32 Mbit. Access speed 100 ns
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DA28F640J5A-1505 Volt Intel StrataFlash Memory
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
5 Volt Intel StrataFlash?? Memory
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
5 Volt Intel StrataFlash?? Memory
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation

Part Number:
Description:
Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel 82801DB I/O Controller Hub (ICH4), Pb-Free SLI
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Intel 82801FB I/O Controller Hub (ICH6)
Manufacturer:
Intel Corporation
Datasheet: